| 规格 | 价格 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Luminescent enzyme substrate
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
用扩展的电子偶联取代C-8位的亚甲基是一种很有前途的制备红移酮肠嗪衍生物的新方法。在本文中,我们描述了一种含氧的coelenterazine衍生物,相对于coelenterazine 400a具有显著的红移(63 nm)生物发光信号最大值(DeepBlueC™,1)。在细胞成像中,含硫coelenterazine衍生物显示出显著的(1.77±0.09;P≤0.01),其发光信号略高于coelenterazine 400a,含氧coelenterazine衍生物的发光信号略高于(0.74±0.08;P≤0.05)较低的发光信号。这有助于进一步了解生物发光的潜在机制。[3]
|
| 细胞实验 |
相对量子产率(RQY)与离体发光动力学[3]
RQY研究和动力学分析使用IVIS动力学进行,该动力学由安装在避光标本室(暗箱)上的冷却电荷耦合器件(CCD)摄像机、摄像机控制器、摄像机冷却系统和计算机控制组成。数据表示为光强(蓝色最弱,红色最强)叠加在灰度参考图像上的伪彩色图像(以光子/s/cm2/scr为单位)。在区域上绘制圆形指定感兴趣区域(roi),并使用Living Image软件将光输出量化为每秒发射的光子总数。 为确定底物的适宜不饱和量,采用10 μL coelenterazine (CTZ) 衍生物1 - 3 (1 ~ 100 μmol/L)和90 μL DMSO或Rluc酶,终浓度为15 nmol/L(生物发光)。将10 μL coelenterazine (CTZ) 衍生物(终浓度为5 μmol/L)与90 μL DMSO或Rluc酶(15 nmol/L)混合在96孔黑板上,以防止孔间光反射,测定RQY和反应动力学。在混合后立即测量发光信号,并使用IVIS监测25-30分钟(发光几乎衰减到接近背景水平)。化学发光每5分钟记录一次光输出,曝光时间30 s;生物发光每1分钟记录一次光输出,前15分钟曝光时间5 s。采用Prism 5.0 GraphPad软件对采集数据进行分析,计算总光输出。在相同条件下,用Tris-HCl缓冲液代替coelenterazine (CTZ) 衍生物溶液作为相应的空白对照。所有试验均为三份。 活细胞发光活性测定[3] 表达Rluc的ES-2细胞(人卵巢癌细胞系)由BioDiagnosis提供。ES-2细胞在Dulbecco's modified Eagle's培养基(DMEM;含10%胎牛血清(FBS)和0.5 μg/mL嘌呤霉素的高葡萄糖(含l-谷氨酰胺),在37℃的湿化气氛中,在5% CO2培养箱中培养。coelenterazine (CTZ) 衍生物在乙醇中溶解成1 mmol/L的原液,用Tris-HCl缓冲液稀释至梯度浓度(5、10、20、40、60、80、100 μmol/L)。 ES-2-Rluc细胞生长于黑色96孔板(每孔4 × 104个细胞)。24小时孵育后,取出培养基。然后用Tris-HCl缓冲液冲洗细胞2次,并用100 μL浓度的coelenterazine (CTZ) 衍生物溶液(范围为0 ~ 100 μmol/L)处理细胞。然后使用IVIS立即确定生物发光信号。每1分钟记录一次光输出,曝光时间30秒,直到发光几乎衰减到接近背景水平。测量每个孔的发光信号(每秒光子数)并绘制平均值。所有的实验都是三次重复。 |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
In conclusion, we have described an oxygen-containing CTZ derivative 2 and it exhibited a more significant red-shifted (63 nm) bioluminescence signal maximum relative to coelenterazine 400a, while it had lower quantum yield. The results of this study appear to support our hypothesis that the introduction of oxygen heteroatom at the C-8 position could also produce a bathochromic effect. While a possible mechanism of the CTZ luminescence reaction has been proposed (Fig. S2 in Supporting information), the enzymatic recognition mechanism of the Rluc system is not yet fully understood. We may surmise that it is due to an efficient extension of p-electron conjugation, electronegativity, or H-bonds of oxygen at the C-8 position. We also developed a new measurement method through an IVIS Kinetic equipped with a CCD to examine RQY. The RQY of CTZ derivative 3 for chemiluminescence is in good agreement with previously reported value. To get a genuine and correct RQY in bioluminescence, we employed commercially available purified Rluc enzyme in place of the rough cytosolic extract to avoid enzyme-independent luminescence. Compounds 2 and 3 showed lower quantum yield that is quite different from previously reported value. However, we discovered compound 3 had a higher affinity to Rluc than coelenterazine 400a. In cell imaging, compound 3 also displayed a higher luminescence signal. In a word, compounds 2 and 3 are promising bright red-shifted CTZ derivatives that provide a novel approach to improve the luminescence properties of CTZ analogs. More significantly, it is beneficial to understand the underlying mechanisms of Rluc bioluminescence upon reacting with coelenterazine.[3]
In BRET2 (Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer), a Renilla luciferase (RLuc) is used as the donor protein, while a Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP2) is used as the acceptor protein. In the presence of the cell permeable substrate DeepBlueC, RLuc emits blue light at 395 nm. If the GFP2 is brought into close proximity to RLuc via a specific biomolecular interaction, the GFP2 will absorb the blue light energy and reemit green light at 510nm. BRET2 signals are therefore easily determined by measuring the ratio of green over blue light (510/395nm) using appropriate dual channel luminometry instruments (e.g., Fusion Universal Microplate Analyzer, Packard BioScience). Since no light source is required for BRET2 assays, the technology does not suffer from high fluorescent background or photobleaching, the common problems associated with standard FRET-based assays. Using BRET2, we developed a generic G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) assay based on the observation that activation of the majority of GPCRs by agonists leads to the interaction of beta-arrestin (a protein that is involved in receptor desensitization and sequestration) with the receptor. We established a cell line stably expressing the GFP2:beta-arrestin 2 fusion protein, and showed that it can be used to monitor the activation of various transiently expressed GPCRs, in BRET2/arrestin assays. In addition, using the HEK 293/GFP2:beta-arrestin 2 cell line as a recipient, we generated a double-stable line co-expressing the vasopressin 2 receptor (V2R) fused to RLuc (V2R:RLuc) and used it for the pharmacological characterization of compounds in BRET2/arrestin assays. This approach yields genuine pharmacology and supports the BRET2/arrestin assay as a tool that can be used with recombinant cell lines to characterize ligand-GPCR interactions which can be applied to ligand identification for orphan receptors.[2] |
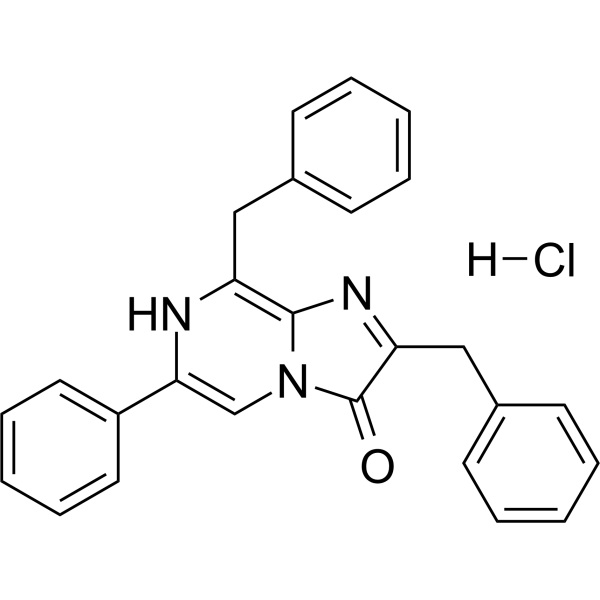
| 分子式 |
C26H22CLN3O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
427.925384998322
|
| 精确质量 |
427.145
|
| CAS号 |
2320429-05-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Coelenteramine 400a;70217-82-2
|
| PubChem CID |
137700438
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| LogP |
0
|
| tPSA |
50.4
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
524
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
UVZGQDPDAXEWQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H21N3O.ClH/c30-26-23(17-20-12-6-2-7-13-20)28-25-22(16-19-10-4-1-5-11-19)27-24(18-29(25)26)21-14-8-3-9-15-21;/h1-15,18,30H,16-17H2;1H
|
| 化学名 |
2,8-dibenzyl-6-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-ol;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
6-phenyl-2,8-bis(phenylmethyl)-imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3(7H)-one,monohydrochloride; 2,8-dibenzyl-6-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-ol;hydrochloride; Coelenteramine 400a (hydrochloride); EX-A9184A; Coelenteramine 400a hydrochloride;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3368 mL | 11.6842 mL | 23.3683 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4674 mL | 2.3368 mL | 4.6737 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2337 mL | 1.1684 mL | 2.3368 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。