| 规格 | 价格 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
GABA reuptake
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
(R) N-[4,4-双(3-甲基-2-噻吩基)丁-3-烯-1-基]尼泊金酸(Tiagabine/NO 328)先前已被证明是小鼠和大鼠的强效抗惊厥药。在这里,我们报告说,NO 328是大鼠前脑突触体制剂(IC50=67 nM)以及神经元和星形胶质细胞原代培养物中γ-[3H]氨基丁酸[(3H]GABA)摄取的强效抑制剂。当NO 328在[3H]GABA摄取之前预孵育时,NO 328对[3H]GABA摄取的抑制显然是混合型的;在没有预孵育的情况下,抑制作用显然是竞争性的。NO 328本身不是GABA摄取载体的底物,但Tiagabine是[3H]GABA摄取的选择性抑制剂。与苯二氮卓受体、组胺H1受体和5-羟色胺1A受体的结合被5-30微M的NO 328抑制,而其他几种受体和摄取位点不受影响。[3H]NO 328在NaCl存在下与大鼠脑膜显示出可饱和和可逆的结合。[3H]NO 328的特异性结合被已知的[3H]GABA摄取抑制剂抑制;然而,GABA和环状氨基酸GABA摄取抑制剂的效力低于预期。这表明结合位点与摄取载体的GABA识别位点不同,而是重叠。[3H]NO 328结合的亲和力常数为18 nM,Bmax为669 pmol/g原始大鼠前脑组织。NaCl依赖性[3H]NO 328结合的区域分布遵循突触体[3H]GABA摄取的区域分布[1]。
我们在体外研究了Tiagabine对大鼠皮质星形胶质细胞基因组DNA的影响。为了评估DNA损伤,我们使用了一种相对简单的技术,称为单细胞凝胶电泳或彗星测定。Tiagabine溶解于培养液中,分别以1、10、20、50 μg/ml的浓度加入培养12 d的星形胶质细胞。替加滨浓度分别为1和10 μg/ml, 48 h后未见DNA损伤。暴露于20 μg/ml抗癫痫药物的细胞出现中度DNA损伤。50 μg/ml替加滨处理后,DNA断裂更为明显。我们得出结论,在通常推荐的剂量下,替加滨似乎不会对皮质大鼠星形胶质细胞产生负面影响,只有在非常高的浓度下才会诱导DNA断裂。[4] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)与包括恐慌在内的焦虑症的病理生理学有关。Tiagabine是一种选择性GABA再摄取抑制剂(SGRI),已被证明可以减轻焦虑症状。这项初步研究评估了噻加宾治疗惊恐障碍患者的疗效和安全性。年龄在18-64岁之间,经DSM-IV诊断为严重至中度惊恐障碍(有或没有广场恐怖症)的男性和女性门诊患者接受了2-20mg/天的开放标签噻加宾治疗,持续10周。结果评估包括Sheehan惊恐障碍量表(SPS)、惊恐障碍严重程度量表(PDSS)、Bandelow恐慌和恐惧症量表(PAS)、汉密尔顿焦虑评定量表(HAM-A)、21分临床医生总体改善量表(CGI-21)、21点患者总体改善(PGI-21)和Sheehan残疾量表(SDS)。在基线时记录得分,此后每周记录一次。在整个研究过程中监测不良事件。在参与该研究的28名患者中,23名患者进行了一次基线后随访,可用于LOCF结果分析。尽管所有结果指标都观察到与基线相比有统计学上的显著降低,但单个量表的百分比改善仅在25-32%的范围内,这在临床上并不显著。Tiagabine通常耐受性良好;最常见的不良反应是恶心、头晕和头痛。只有一名患者因不良事件而停药。这些发现表明,服用噻加宾对惊恐障碍患者可能没有什么好处。[2]
噻加滨对灰色和白色结构中GABA摄取的影响[3] 为了确定参与白质高亲和力GABA摄取的GABA转运蛋白的类型,我们研究了GABA摄取对Tiagabine的敏感性。Tiagabine是GAT-1 GABA转运蛋白的选择性抑制剂,Ki为∼0.1μM(Thomsen等人,1997),可抑制颞叶皮层和白色结构中的高亲和力GABA摄取(图1B)。在0.1μM时,由颞皮层制成的蛋白脂质体中的高亲和力GABA摄取被抑制了约50%。在白色结构中,0.1μM的噻加宾引起了60-68%的抑制,这明显大于颞叶皮层中的抑制(图1B)。即使在0.33μM的浓度下,与颞叶皮层相比,噻加宾在胼胝体、锥体束和枕叶皮层下的白质中的高亲和力GABA摄取受到的抑制程度略高(图1B)。 |
| 细胞实验 |
以1±2日龄Wistar大鼠为材料制备星形胶质细胞原代培养物,将其去头,并按照Cardile等人的描述获得细胞。星形胶质细胞在含有10%胎牛血清、1 mM l -谷氨酰胺和抗生素的Dulbecco's modi®ed Eagle's培养基/F12培养基中培养,并在湿度为5% CO2/ 95%的环境中于378C培养。在第12天,分别考虑不同的细胞板,作为未处理的对照或Tiagabine处理的星形胶质细胞。为了评估细胞的星形胶质性质,在治疗开始前进行glial®briral酸性蛋白检测。在本研究中,仅考虑了胶质®briral酸性蛋白免疫染色显示90±95%的细胞为星形胶质细胞的培养数据。根据Singh等人的方法使用Comet测定法,很少使用莫迪离子。单层星形胶质细胞(未处理对照和不同Tiagabine处理48 h)用pH 7.4的磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS)洗涤两次,用橡胶警棍刮碟悬浮在2ml PBS中,800 g离心15分钟。将球团重新悬浮在小体积PBS中,将细胞的等分物与0.4%台锥蓝溶液混合并计数。剩余的细胞考虑进行彗星试验。显微镜载玻片用100%甲醇清洗,风干,用1% (w/v)标准熔点琼脂糖(NMA)和solidi®ed溶液冲洗。10微升细胞悬液(0.8±1磅105个细胞)与75毫升0.5%低熔点琼脂糖(LMA)混合,并在载玻片上染色。然后加入第三层85 ml LMA。在48℃的低温裂解液(N-laurosil-sarcosine 1%, NaCl 2.5 M, Na2EDTA 10 mM, Triton X-100 1%, DMSO 10%, (pH 10))中浸泡1小时,在高pH缓冲液(NaOH 300 mM, Na2EDTA 1 mM)中变性20分钟,在25 V的冰浴和半暗条件下在相同的缓冲液中运行25分钟。电泳结束时,载玻片在中和缓冲液(Tris±HCl 0.4 M, (pH 7.5))中轻轻洗涤三次,用100 ml溴化乙啶(2mg /ml)染色10分钟,并用18磅18毫米的盖玻片覆盖;过量的染料被吸收了。这些载玻片要么立即进行评分,使用与计算机连接的雷茨荧光显微镜。[4]
|
| 动物实验 |
High-affinity uptake of [3H]GABA into proteoliposomes and fresh homogenates [3]
Plasma membrane transporters for GABA were reconstituted in proteoliposomes according to the method of Danbolt et al. (1990) as described (Trotti et al., 1995, Hassel et al., 2003), starting from 10% homogenates (w/v) in sucrose, 0.32 M. These proteoliposomes have an internal buffer of KCl, 140 mM. Uptake of [3H]GABA, 0.5 μM, final specific activity 5.6 mCi/μmol, was performed in triplicates in the presence of NaCl, 150 mM, and valinomycin, 1 μM, for 15 min at 30 °C; the sequestered radioactivity was trapped on filter paper and quantified by scintillation counting. Blanks were run in duplicates for each structure and were obtained by keeping the samples on ice and adding the sodium ionophore nigericin, 1 μM. Uptake was linear with time for at least 20 min. Previously, uptake by proteoliposomes made from frozen brain tissue has been shown to be the same as for fresh brain homogenates when [3H]glutamate was the transported compound (Hassel et al., 2003), suggesting that freezing does not affect transport activities. The sensitivity of high-affinity GABA uptake to Tiagabine was investigated in temporal cortex and white structures. Tiagabine, a selective inhibitor of the GAT-1 GABA transporter, with a Ki of 0.1 μM (Thomsen et al., 1997), was added during incubation at 0.1 or 0.33 μM. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Tiagabine is nearly completely absorbed (>95%). Approximately 2% of an oral dose of tiagabine is excreted unchanged, with 25% and 63% of the remaining dose excreted into the urine and feces, respectively, primarily as metabolites. 109 mL/min [Healthy subjects] Absorption of tiagabine is rapid, with peak plasma concentrations occurring at approximately 45 minutes following an oral dose in the fasting state. Tiagabine is nearly completely absorbed (>95%), with an absolute oral bioavailability of about 90%. A high fat meal decreases the rate (mean T max was prolonged to 2.5 hours, and mean C max was reduced by about 40%) but not the extent (AUC) of tiagabine absorption. The pharmacokinetics of tiagabine are linear over the single dose range of 2 to 24 mg. Following multiple dosing, steady state is achieved within 2 days. Tiagabine is 96% bound to human plasma proteins, mainly to serum albumin and alpha1-acid glycoprotein over the concentration range of 10 ng/mL to 10,000 ng/mL. While the relationship between tiagabine plasma concentrations and clinical response is not currently understood, trough plasma concentrations observed in controlled clinical trials at doses from 30 to 56 mg/day ranged from <1 ng/mL to 234 ng/mL. A diurnal effect on the pharmacokinetics of tiagabine was observed. Mean steady-state C min values were 40% lower in the evening than in the morning. Tiagabine steady-state AUC values were also found to be 15% lower following the evening tiagabine dose compared to the AUC following the morning dose. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for TIAGABINE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Tiagabine is likely metabolized primarily by the 3A isoform subfamily of hepatic cytochrome P450. Although the metabolism of tiagabine has not been fully elucidated, in vivo and in vitro studies suggest that at least two metabolic pathways for tiagabine have been identified in humans: 1) thiophene ring oxidation leading to the formation of 5-oxo-tiagabine; and 2) glucuronidation. The 5-oxo-tiagabine metabolite does not contribute to the pharmacologic activity of tiagabine. Based on in vitro data, tiagabine is likely to be metabolized primarily by the 3A isoform subfamily of hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP 3A), although contributions to the metabolism of tiagabine from CYP 1A2, CYP 2D6 or CYP 2C19 have not been excluded. Tiagabine is likely metabolized primarily by the 3A isoform subfamily of hepatic cytochrome P450. Route of Elimination: Approximately 2% of an oral dose of tiagabine is excreted unchanged, with 25% and 63% of the remaining dose excreted into the urine and feces, respectively, primarily as metabolites. Half Life: 7-9 hours Biological Half-Life 7-9 hours ... The average elimination half-life for tiagabine in healthy subjects ranged from 7 to 9 hours. The elimination half-life decreased by 50 to 65% in hepatic enzyme-induced patients with epilepsy compared to uninduced patients with epilepsy. Its half-life is about 8 hrs but is shortened by 2 to 3 hrs when coadministered with hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs such as phenobarbital, phenytoin, or carbamazepine. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Though the exact mechanism by which Tiagabine exerts its effect on the human body is unknown, it does appear to operate as a selective GABA reuptake inhibitor. Hepatotoxicity Limited data are available on the hepatotoxicity of tiagabine. In clinical trials, therapy with tiagabine was not associated with an increased frequency of serum aminotransferase elevations or liver toxicity. No individual case reports of liver injury from tiagabine have been published and its use has not been associated with hypersensitivity syndromes or autoimmunity. However, its overall use has been limited. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Monitor the infant for drowsiness, adequate weight gain, and developmental milestones, especially in younger, exclusively breastfed infants and when using combinations of anticonvulsant or psychotropic drugs. Because there is very limited published experience with tiagabine during breastfeeding, other agents may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants One mother breastfed her infant while taking tiagabine 24 mg and then 20 mg daily. No adverse effects were reported in 10 newborns who were 4 to 23 days old who were breastfed during maternal intake of levetiracetam 1000 to 3000 mg daily. One mother was also taking tiagabine 30 mg daily, clobazam 45 mg daily and oxcarbazepine 600 mg daily. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 96% Interactions /Concomitant administration of tiagabine with/ alcohol or central nervous system depression-producing medications may increase CNS depression. Tiagabine clearance is increased by 60% in patients taking carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, or primidone. Tiagabine causes a slight decrease (about 10%) in steady-state valproate concentrations; in vitro studies have shown that valproate decreases the protein binding of tiagabine from 96.3 to 94.8, resulting in an increase of approximately 40% in the free tiagabine concentration; clinical relevance of this finding is unknown. Co-administration of cimetidine (800 mg/day) to patients taking tiagabine chronically had no effect on tiagabine pharmacokinetics. For more Interactions (Complete) data for TIAGABINE (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. (R)-N-[4,4-bis(3-methyl-2-thienyl)but-3-en-1-yl]nipecotic acid binds with high affinity to the brain gamma-aminobutyric acid uptake carrier. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):639-47.
[2]. An open-label study of tiagabine in panic disorder. Psychopharmacol Bull, 2007. 40(3): p. 32-40. [3]. High-affinity GABA uptake and GABA-metabolizing enzymes in pig forebrain white matter: a quantitative study. Neurochem Int, 2007. 50(2): p. 365-70. [4]. Tiagabine treatment and DNA damage in rat astrocytes: an in vitro study by comet assay. Neurosci Lett. 2001 Jun 22;306(1-2):17-20. |
| 其他信息 |
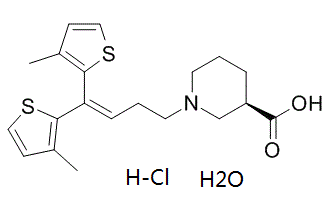
Tiagabine is a piperidinemonocarboxylic acid that is (R)-nipecotic acid in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen has been replaced by a 1,1-bis(3-methyl-2-thienyl)but-1-en-4-yl group. A GABA reuptake inhibitor, it is used (generally as the hydrochloride salt) for the treatment of epilepsy. It has a role as a GABA reuptake inhibitor and an anticonvulsant. It is a piperidinemonocarboxylic acid, a beta-amino acid, a member of thiophenes and a tertiary amino compound. It is functionally related to a (R)-nipecotic acid. It is a conjugate base of a tiagabine(1+).
Tiagabine is an anti-convulsive medication. It is also used in the treatment for panic disorder as are a few other anticonvulsants. Though the exact mechanism by which tiagabine exerts its effect on the human body is unknown, it does appear to operate as a selective GABA reuptake inhibitor. Tiagabine is an Anti-epileptic Agent. The physiologic effect of tiagabine is by means of Decreased Central Nervous System Disorganized Electrical Activity. Tiagabine is a unique anticonvulsant used largely as an adjunctive agent in therapy of partial seizures in adults or children. Therapy with tiagabine is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, and clinically apparent liver injury from tiagabine has not been reported and must be rare if it occurs at all. Tiagabine is an anti-convulsive medication. It is also used in the treatment for panic disorder as are a few other anticonvulsants. Though the exact mechanism by which tiagabine exerts its effect on the human body is unknown, it does appear to operate as a selective GABA reuptake inhibitor. A nipecotic acid derivative that acts as a GABA uptake inhibitor and anticonvulsant agent. It is used in the treatment of EPILEPSY, for refractory PARTIAL SEIZURES. See also: Tiagabine Hydrochloride (has salt form); Tiagabine hydrochloride monohydrate (is active moiety of). Drug Indication For the treatment of partial seizures FDA Label Mechanism of Action Though the exact mechanism by which Tiagabine exerts its effect on the human body is unknown, it does appear to operate as a selective GABA reuptake inhibitor. Although the precise mechanism of action of tiagabine is unknown, the drug enhances inhibitory neurotransmission mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Tiagabine increases the amount of GABA available in extracellular spaces of the globus pallidus, ventral pallidum, and substantia nigra, suggesting a GABA-mediated anticonvulsant mechanism of action (i.e., inhibition of neural impulse propagations that contribute to seizures). Tiagabine inhibits presynaptic neuronal and glial GABA reuptake, and increases the amount of GABA available for postsynaptic receptor binding. The drug does not stimulate GABA release, and does not have activity at other receptor binding and uptake sites at concentrations that inhibit the uptake of GABA. Tiagabine selectively blocks presynaptic GABA uptake by binding reversibly and saturably to recognition sites associated with GABA transporter protein in neuronal and glial membranes. In vitro binding studies indicate that tiagabine does not inhibit substantially the uptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, glutamate, or choline, and does not bind substantially to dopamine D1 or D2; cholinergic muscarinic; serotonergic type 1A, type 2, or type 3 (5HT1A, 5HT2, or 5HT3, respectively); alpha1- or alpha2-adrenergic; beta1- or beta2-adrenergic; histamine H2 or H3; adenosine A1 or A2; opiate mu or kappa1; glutamate N-methyl-d- aspartate (NMDA); or GABAA receptors. Also, tiagabine has little or no affinity for sodium or calcium channels. Tiagabine binds to histamine H1, serotonergic type 1B (5HT1B), benzodiazepine, and chloride channel receptors at concentrations 20-400 times those that inhibit the uptake of GABA. Therapeutic Uses Tiagabine is indicated as an adjunct to other anticonvulsant medications in the treatment of partial seizures in adults and children 12 years of age and older. /Included in US product label/ Drug Warnings Although tiagabine reduces the frequency of seizures in patients with epilepsy, use of the drug has been associated with a paradoxical occurrence of seizures in patients without a history of epilepsy. Post-marketing reports have shown that /tiagabine/ use has been associated with new onset seizures and status epilepticus in patients without epilepsy. Dose may be an important predisposing factor in the development of seizures, although seizures have been reported in patients taking daily doses of /tiagabine/ as low as 4 mg/day. In most cases, patients were using concomitant medications (antidepressants, antipsychotics, stimulants, narcotics) that are thought to lower the seizure threshold. Some seizures occurred near the time of a dose increase, even after periods of prior stable dosing. The /tiagabine/ dosing recommendations in current labeling for treatment of epilepsy were based on use in patients with partial seizures 12 years of age and older, most of whom were taking enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs (AEDs; e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, primidone and phenobarbital) which lower plasma levels of /tiagabine/ by inducing its metabolism. Use of /tiagabine/ without enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs results in blood levels about twice those attained in the studies on which current dosing recommendations are based Safety and effectiveness of /tiagabine/ have not been established for any indication other than as adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in adults and children 12 years and older. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TIAGABINE (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Tiagabine is used primarily as an anticonvulsant for the adjunctive treatment of epilepsy. The precise mechanism by which Tiagabine exerts its antiseizure effect is unknown, although it is believed to be related to its ability to enhance the activity of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Tiagabine binds to recognition sites associated with the GABA uptake carrier. It is thought that, by this action, Tiagabine blocks GABA uptake into presynaptic neurons, permitting more GABA to be available for receptor binding on the surfaces of post-synaptic cells. On the basis of the present and previous our results, we may conclude that Tiagabine, at the usual recommended doses, does not appear to influence negatively the cortical rat astrocytes, inducing DNA fragmentation only at very high concentrations. However, since astrocytes are resistant to oxidative stress more than neurons, it cannot be excluded that neuronal DNA fragmentation may be induced by Tiagabine at lower concentrations.[4] |
| 分子式 |
C20H28CLNO3S2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
430.024222373962
|
| 精确质量 |
429.119
|
| CAS号 |
145821-57-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Tiagabine hydrochloride;145821-59-6;Tiagabine;115103-54-3
|
| PubChem CID |
67065562
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
98
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
474
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
CC1=C(SC=C1)C(=CCCN2CCC[C@H](C2)C(=O)O)C3=C(C=CS3)C.O.Cl
|
| InChi Key |
KOZCGZMZXXVHCF-GGMCWBHBSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H25NO2S2.ClH.H2O/c1-14-7-11-24-18(14)17(19-15(2)8-12-25-19)6-4-10-21-9-3-5-16(13-21)20(22)23;;/h6-8,11-12,16H,3-5,9-10,13H2,1-2H3,(H,22,23);1H;1H2/t16-;;/m1../s1
|
| 化学名 |
(3R)-1-[4,4-bis(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)but-3-enyl]piperidine-3-carboxylic acid;hydrate;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
NO050328 hydrochloride hydrate; NNC-05-0328; NNC-050328; NO 329; NO-05-0328; NO329; trade name Gabitril
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3255 mL | 11.6274 mL | 23.2547 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4651 mL | 2.3255 mL | 4.6509 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2325 mL | 1.1627 mL | 2.3255 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。