| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
DPP-IV (IC50 = 3.5 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
维格列汀抑制细胞凋亡以增加 β 细胞的存活率。此外,维格列汀还能刺激细胞分裂[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
当以 35 mg/kg 的剂量每天口服一次时,维格列汀会升高 db/db 小鼠胰岛中的血浆活性 GLP-1 水平 [2]。维格列汀(10 µmol/kg;口服)在肥胖雄性 Zucker 大鼠中可显着降低血糖波动并增加胰岛素分泌 [1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
DPP-IV体外抑制测定。大鼠、人类、猴子血浆测定。[4]
在该试验中,人、大鼠或猴子血浆用作DPP-IV的来源。标准测定法是从之前发表的方法修改而来的。将5μL血浆加入96孔平底微量滴定板中,然后在测定缓冲液(25 mM HEPES,140 mM NaC1,1%RIA级BSA,pH 7.8)中加入5μL 80 mM MgC12。在室温下预孵育5分钟后,通过加入10μL含有0.1 mM底物(H-Gly-Pro-AMC;AMC为7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素)的测定缓冲液来引发反应。用铝箔覆盖板(或置于黑暗中),在室温下孵育20分钟。孵育后,使用CytoFluor II荧光计测量荧光(激发380nm/发射460nm)。添加2μL供试化合物和溶剂对照,并将测定缓冲液体积减少至13μL。使用0-50μM AMC溶液生成游离AMC的标准曲线。生成的线性曲线用于插值底物消耗量(催化活性,单位为nmoles底物裂解/min)。 体外DPP-II抑制测定。[4] 牛肾匀浆提取物经离子交换和腺苷脱氨酶层析部分纯化后,用作DPP-II的来源。标准测定法是从之前发表的方法修改而来的。47将20微克含DPP II的级分在测定缓冲液(0.2 M硼酸盐,0.05 M柠檬酸盐,pH 5.3)中稀释至最终体积为60μL,加入96孔平底微量滴定板,然后加入10μL 10 mM邻菲咯啉(以抑制氨基肽酶活性)和20μL 5 mM底物(H-Lys-Ala-AMC;AMC为7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素)。将平板在37°C下孵育30分钟。孵育后,使用CytoFluor II荧光计测量荧光(激发380 nm/发射460 nm)。以20μL的添加量添加试验化合物和溶剂对照,并将测定缓冲液体积减少到50μL。使用0至100μM的AMC生成AMC的标准曲线。生成的线性曲线用于插值催化活性(以nmoles底物切割/min为单位)。 Vildagliptin (LAF-237; NVP-LAF 237) 的 IC50 为 2.3 nM,抑制 DPP-4。图2代表维格列汀,一种N-取代的甘氨酰-2-氰基吡咯烷。它的抑制浓度 (IC50) 约为 2–3 nmol/L,在体外对人类和啮齿类动物来说是一种强效、可逆、竞争性的 DPP-4 抑制剂。至关重要的是,与其他类似肽酶相比,维格列汀对 DPP-4 表现出高特异性抑制,其 IC50 超过 200 mol/L。 |
| 细胞实验 |
体外研究。体外DPP-IV抑制测定:Caco-2测定。[4]
在该试验中,使用人结肠癌细胞提取物(Caco-2 ATCC HTB 37)作为DPP-IV的来源。如前所述,分化细胞以诱导DPP-IV表达。细胞提取物由溶解在裂解缓冲液(10 mM Tris-HC1,0.15 M NaC1,0.04 T.I.U.(胰蛋白酶抑制剂单位)抑肽酶,0.5%非检测-P40,pH 8.0)中的细胞制备,然后在4°C下以35 000g离心30分钟以去除细胞碎片。通过向96孔平底微量滴定板中加入20μg溶解的Caco-2蛋白进行测定,该蛋白在测定缓冲液(25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4,140 mM NaC1,10 mM KC1,1%牛血清白蛋白)中稀释至最终体积为125μL。通过加入25μL 1 mM底物(H-Ala-Pro-pNA;pNA为对硝基苯胺)引发反应。反应在室温下进行10分钟,然后加入19μL的25%冰醋酸以停止反应。使用CytoFluor II荧光计测量荧光(激发380nm/发射460nm)。试验化合物和溶剂对照以30μL的加入量加入,测定缓冲液体积减少至95μL。在测定缓冲液中使用0-100μM pNA生成游离对硝基苯胺的标准曲线。生成的线性曲线用于插值底物消耗量(催化活性,单位为nmoles底物裂解/min)。 体外脯氨酸切割酶(PPCE)后抑制测定。[4] 通过离子交换色谱法部分纯化的人红细胞胞浆提取物用作PPCE的来源。标准测定法是从之前发表的方法修改而来的。将含PPCE的组分(350 ng蛋白质)在测定缓冲液(20 mM NaPO4、0.5 mM EDTA、0.5 mM DTT、1%BSA,pH 7.4)中稀释至最终体积为90μL,加入96孔平底微量滴定板,然后加入10μL 0.5 mM底物(Z-Gly-Pro-AMC;AMC为7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素)。将平板在室温下孵育30分钟。孵育后,使用CytoFluor II荧光计测量荧光(激发380nm/发射460nm)。试验化合物和溶剂对照以20μL的添加量加入,测定缓冲液体积减少到70μL。使用0至5μM的AMC溶液生成游离AMC的标准曲线。生成的线性曲线用于插值催化活性(以nmoles底物切割/min为单位)。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male db/db mice (BKS) and wild-type mice [2]
Doses: 35 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day; for 6 weeks Experimental Results: Increased plasma active GLP-1 levels (22.63±1.19 vs. 11.69±0.44). Animal/Disease Models: Obese male Zucker rat [1] Doses: 10 µmol/kg (pharmacokinetic/PK/PK analysis) Route of Administration: Oral Experimental Results:Dramatically diminished blood sugar fluctuations and stimulated insulin secretion. In Vivo Obese Male (fa/fa) Zucker Rat Studies.[1] Effect of Vildagliptin (NVP LAF 237; DSP7238; LAF237) (Vildagliptin (NVP LAF 237; DSP7238; LAF237) ) on DPP-IV Activity, Active GLP-1 Levels, and Glucose and Insulin Excursions. Studies were performed on obese male Zucker (fa/fa) rats (Charles River Labs, Cambridge, MA); controls (n = 9) and Vildagliptin (NVP LAF 237; DSP7238; LAF237) -treated (n = 9). These rats were purchased at 7 weeks of age, cannulated at 7.5 weeks, and studied beginning at around 11 weeks of age. In the morning of the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), the rats were “fasted” by removing food before the lights were turned on, after which they were transferred to the experiment room at 8:00 a.m.. Vildagliptin (NVP LAF 237; DSP7238; LAF237) was dissolved in vehicle solution (0.5% carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and 0.2% Tween 80). The cannulas were connected to sampling tubing (PE-100, 0.034 in. i.d. × 0.06 in. o.d.), which were filled with saline. After 30−40 min cage acclimation, a 0.5 mL baseline blood sample was taken at t = −15 min, and the rats were then orally dosed with CMC or Vildagliptin (NVP LAF 237; DSP7238; LAF237) (10 μmol/kg), after which additional baseline blood samples were taken at t = −5, −2.5, and 0 min. The animals were then administered an oral glucose solution (10% glucose, 1 g/kg) immediately after t = 0‘. The rest of the samples were taken at 1, 3, 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 min. Throughout the OGTT, an equal volume of donor blood was used to replace the blood withdrawn during sampling. Donor blood was obtained from donor rats through cardiac puncture. The collected blood samples (0.5 mL) were immediately transferred into chilled Eppendorf tubes containing 50 μL of EDTA: trasylol (25 mg/mL of 10 000 trasylol) and used for the measurement of glucose and insulin levels and DPP-IV activity. Larger blood samples (0.75 mL) were collected at t = −15, 0, 5, 10, 15, and 30 min for GLP-1 (7−36 amide) measurements. To these tubes, the DPP-IV inhibitor valine pyrrolidide was added to yield a final concentration in the blood of 1 μM. Technical difficulties with obtaining blood samples after minute 20 for one rat in both the CMC and Vildagliptin (NVP LAF 237; DSP7238; LAF237) groups resulted in the inability to calculate glucose and insulin AUC data for those rats, leading to AUC data with an n = 8/group. Measurement of plasma glucose was made using a modification of a Sigma Diagnostics glucose oxidase kit. DPP-IV activity was measured in plasma samples obtained at −5, 0, 20, 45, and 90 min DPP-IV activity as previously described in the above ex vivo rat plasma experimental. Plasma levels of GLP-1 (7−36 amide) were measured using the GLP-1 (active) Elisa Kit. In Vivo Cynomolgus Monkey PK/PD Studies Using 8c and Vildagliptin (NVP LAF 237; DSP7238; LAF237) . [1] Ketamine-anesthetized male healthy cynomolgus monkeys received either 8c (n = 2) or Vildagliptin (NVP LAF 237; DSP7238; LAF237) (n = 3) (dissolved in CMC/Tween-80) by oral gavage (1.007 μmol/kg), and by intravenous administration (0.399 μmol/kg) (dissolved in saline). For iv study, compound was administered (0.4 mL/kg over 1 min) in 0.9% saline as vehicle. Different monkeys were used for each dosage regimen. Basal blood samples were collected at −10 min and immediately prior to administration of compound. Blood samples were collected at 0.03, 0.08, 0.17, 0.25, 0.33, 0.42, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.25, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 7, 12, and 25 h postdose for both routes of administration. Blood was obtained into heparin-coated syringes, transferred to microcentrifuge tubes, and centrifuged to separate the plasma. The plasma was stored at −80 °C in fresh microcentrifuge tubes until assay. DPP-IV activity was measured in a similar manner was as previously described in the above ex vivo rat and human plasma experimentals. Plasma DPP-IV activities were calculated and expressed as ‘percent of baseline' to reduce variability due to individual differences in plasma enzyme activity. Area-under-curve (AUC) values for DPP-IV activity were calculated from time (hours after dose) vs effect (percent inhibition) curves from individual animals using the trapezoidal method. The ratio of dose-normalized effect AUC for oral/intravenous administration routes was taken as an estimate of effect bioavailability. Parent drug concentrations were determined using an HPLC/MS/MS method with a limit of quantification of 1 ng/mL. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using noncompartment modeling, and the AUC was calculated using the linear trapezoidal method. Absolute oral bioavailability was calculated by (AUC0-∞po × 399)/(AUC0-∞iv × 1007). Vildagliptin was orally administered to db/db mice for 6 weeks, followed by evaluation of beta cell apoptosis by caspase3 activity and TUNEL staining method. Endoplasmic reticulum stress markers were determined with quantitative RT-PCR, immunohistochemistry and immunoblot analysis. Results: After 6 weeks of treatment, vildagliptin treatment increased plasma active GLP-1 levels (22.63±1.19 vs. 11.69±0.44, P<0.001), inhibited beta cell apoptosis as demonstrated by lower amounts of TUNEL staining nuclei (0.37±0.03 vs. 0.55±0.03, P<0.01) as well as decreased caspase3 activity (1.48±0.11 vs. 2.67±0.13, P<0.01) in islets of diabetic mice compared with untreated diabetic group. Further, vildagliptin treatment down-regulated several genes related to endoplasmic reticulum stress including TRIB3 (tribbles homolog 3) (15.9±0.4 vs. 33.3±1.7, ×10⁻³, P<0.001), ATF-4(activating transcription factor 4) (0.83±0.06 vs. 1.42±0.02, P<0.001) and CHOP(C/EBP homologous protein) (0.07±0.01 vs. 0.16±0.01, P<0.001). Conclusions: Vildagliptin promoted beta cell survival in db/db mice in association with down-regulating markers of endoplasmic reticulum stress including TRIB3, ATF-4 as well as CHOP.[5] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption
In a fasting state, vildagliptin is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are observed at 1.7 hours following administration. Plasma concentrations of vildagliptin increase in an approximately dose-proportional manner. Food delays Tmax to 2.5 hours and decreases Cmax by 19%, but has no effects on the overall exposure to the drug (AUC). Absolute bioavailability of vildagliptin is 85%. Route of Elimination Vildagliptin is eliminated via metabolism. Following oral administration, approximately 85% of the radiolabelled vildagliptin dose was excreted in urine and about 15% of the dose was recovered in feces. Of the recovered dose in urine, about 23% accounted for the unchanged parent compound. Volume of Distribution The mean volume of distribution of vildagliptin at steady-state after intravenous administration is 71 L, suggesting extravascular distribution. Clearance After intravenous administration to healthy subjects, the total plasma and renal clearance of vildagliptin were 41 and 13 L/h, respectively. Metabolism / Metabolites About 69% of orally administered vildagpliptin is eliminated via metabolism not mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Based on the findings of a rat study, DPP-4 contributes partially to the hydrolysis of vildagliptin. Vildagliptin is metabolized to pharmacologically inactive cyano (57%) and amide (4%) hydrolysis products in the kidney. LAY 151 (M20.7) is a major inactive metabolite and a carboxylic acid that is formed via hydrolysis of the cyano moiety: it accounts for 57% of the dose. Other circulating metabolites reported are an N-glucuronide (M20.2), an N-amide hydrolysis product (M15.3), two oxidation products, M21.6 and M20.9. Biological Half-Life The mean elimination half-life following intravenous administration is approximately two hours. The elimination half-life after oral administration is approximately three hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
The plasma protein binding of vildagliptin is 9.3%. Vildagliptin distributes equally between plasma and red blood cells. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Vildagliptin is an amino acid amide.
Vildagliptin (LAF237) is an orally active antihyperglycemic agent that selectively inhibits the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enzyme. It is used to manage type II diabetes mellitus, where GLP-1 secretion and insulinotropic effects are impaired. By inhibiting DPP-4, vildagliptin prevents the degradation of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), which are incretin hormones that promote insulin secretion and regulate blood glucose levels. Elevated levels of GLP-1 and GIP consequently results in improved glycemic control. In clinical trials, vildagliptin has a relatively low risk of hypoglycemia. Oral vildagliptin was approved by the European Medicines Agency in 2008 for the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus in adults as monotherapy or in combination with [metformin], a sulfonylurea, or a thiazolidinedione in patients with inadequate glycemic control following monotherapy. It is marketed as Galvus. Vildagliptin is also available as Eucreas, a fixed-dose formulation with metformin for adults in who do not adequately glycemic control from monotherapy. Vildagliptin is currently under investigation in the US.
Vildagliptin is a cyanopyrrolidine-based, orally bioavailable inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4), with hypoglycemic activity. Vildagliptin's cyano moiety undergoes hydrolysis and this inactive metabolite is excreted mainly via the urine. A pyrrolidine-carbonitrile derivative and potent inhibitor of DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE 4 that is used in the treatment of TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS. Drug Indication Vildagliptin is indicated in the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus in adults. As monotherapy, vildagliptin is indicated in adults inadequately controlled by diet and exercise alone and for whom metformin is inappropriate due to contraindications or intolerance. It is also indicated as dual therapy in combination with metformin, a sulphonylurea, or a thiazolidinedione in adults patients with insufficient glycemic control despite maximal tolerated dose of monotherapy. Vildagliptin is also marketed in a combination product with [metformin] for the treatment of adults with type II diabetes mellitus who inadequately respond to either monotherapy of vildagliptin or metformin. This fixed-dose formulation can be used in combination with a sulphonylurea or insulin (i.e., triple therapy) as an adjunct to diet and exercise in adults who do not achieve adequate glycemic control with monotherapy or dual therapy. Vildagliptin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycaemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: as monotherapy in patients in whom metformin is inappropriate due to contraindications or intolerance. in combination with other medicinal products for the treatment of diabetes, including insulin, when these do not provide adequate glycaemic control (see sections 4. 4, 4. 5 and 5. 1 for available data on different combinations). Vildagliptin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycaemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: as monotherapy in patients in whom metformin is inappropriate due to contraindications or intolerance. in combination with other medicinal products for the treatment of diabetes, including insulin, when these do not provide adequate glycaemic control. Pharmacodynamics Vildagliptin works to improve glycemic control in type II diabetes mellitus by enhancing the glucose sensitivity of beta-cells (β-cells) in pancreatic islets and promoting glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Increased GLP-1 levels leads to enhanced sensitivity of alpha cells to glucose, promoting glucagon secretion. Vildagliptin causes an increase in the insulin to glucagon ratio by increasing incretin hormone levels: this results in a decrease in fasting and postprandial hepatic glucose production. Vildagliptin does not affect gastric emptying. It also has no effects on insulin secretion or blood glucose levels in individuals with normal glycemic control. In clinical trials, treatment with vildagliptin 50-100 mg daily in patients with type 2 diabetes significantly improved markers of beta-cells, proinsulin to insulin ratio, and measures of beta-cell responsiveness from the frequently-sampled meal tolerance test. Vildagliptin has improves glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels. Mechanism of Action Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) are incretin hormones that regulate blood glucose levels and maintain glucose homeostasis. It is estimated that the activity of GLP-1 and GIP contribute more than 70% to the insulin response to an oral glucose challenge. They stimulate insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner via G-protein-coupled GIP and GLP-1 receptor signalling. In addition to their effects on insulin secretion, GLP-1 is also involved in promoting islet neogenesis and differentiation, as well as attenuating pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis. Incretin hormones also exert extra-pancreatic effects, such as lipogenesis and myocardial function. In type II diabetes mellitus, GLP-1 secretion is impaired, and the insulinotropic effect of GIP is significantly diminished. Vildagliptin exerts its blood glucose-lowering effects by selectively inhibiting dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), an enzyme that rapidly truncates and inactivates GLP-1 and GIP upon their release from the intestinal cells. DPP-4 cleaves oligopeptides after the second amino acid from the N-terminal end. Inhibition of DPP-4 substantially prolongs the half-life of GLP-1 and GIP, increasing the levels of active circulating incretin hormones. The duration of DPP-4 inhibition by vildagliptin is dose-dependent. Vildagliptin reduces fasting and prandial glucose and HbA1c. It enhances the glucose sensitivity of alpha- and beta-cells and augments glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Fasting and postprandial glucose levels are decreased, and postprandial lipid and lipoprotein metabolism are also improved. |
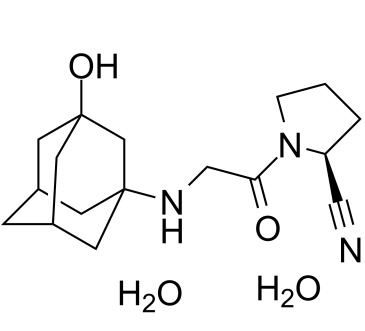
| 分子式 |
C17H27N3O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
321.41458439827
|
| 精确质量 |
339.215
|
| CAS号 |
2133364-01-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Vildagliptin;274901-16-5;(2R)-Vildagliptin;1036959-27-9
|
| PubChem CID |
167996054
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
78.4
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
523
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
N(C12CC3CC(CC(C3)(O)C1)C2)CC(N1CCC[C@H]1C#N)=O.O
|
| InChi Key |
MVOBUCAQTXEOGS-XQOPLDTQSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H25N3O2.2H2O/c18-9-14-2-1-3-20(14)15(21)10-19-16-5-12-4-13(6-16)8-17(22,7-12)11-16;;/h12-14,19,22H,1-8,10-11H2;2*1H2/t12-,13+,14-,16?,17?;;/m0../s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-1-[2-[[(5S,7R)-3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl]amino]acetyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile;dihydrate
|
| 别名 |
LAF-237 dihydrate; Vildagliptin dihydrate; 2133364-01-7; (2S)-1-[2-[[(5S,7R)-3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl]amino]acetyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile;dihydrate NVPLAF 237 dihydrate; LAF 237 dihydrate NVP-LAF-237 dihydrate; LAF237 dihydrate; NVP-LAF 237 dihydrate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1113 mL | 15.5565 mL | 31.1129 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6223 mL | 3.1113 mL | 6.2226 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3111 mL | 1.5556 mL | 3.1113 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04410341 | Recruiting | Drug: Vildagliptin 50 MG Drug: Escitalopram 20 mg |
Major Depressive Disorder | Sadat City University | May 1, 2020 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT05429554 | Recruiting | Drug: Vildagliptin | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | MTI University | June 2022 | |
| NCT04761861 | Recruiting | Drug: Vildagliptin 50 MG Drug: Placebo |
Schizophrenia Dyslipidemias |
Sadat City University | February 16, 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03925701 | Recruiting | Drug: Vildagliptin Drug: vildagliptin\metformin |
dm | Sherief Abd-Elsalam | April 1, 2019 | Phase 3 |
| NCT06068686 | Recruiting | Drug: Vildagliptin 50 MG Drug: Glimepiride 3 Mg Oral Tablet |
Type 2 Diabetes | Damanhour University | October 1, 2022 | Not Applicable |