| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
溴芬酸(0-80 μg/mL;24 小时)以浓度依赖性方式抑制转化生长因子-β2 诱导的 HLEC-B3 上皮细胞向间质细胞的转变 [2]。在人前囊中,转化生长因子-β2 诱导的上皮间质转化受到溴芬酸(80 μg/mL;48 小时)的抑制 [2]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
用溴芬酸溶液(0.0032-3.16%;100 或 200 μL;擦在背部)处理的大鼠在浓度低至 0.1%(处理前 4 小时)或 0.32%(处理前 18 小时)时表现出显着的抗菌活性。炎症[3]。当局部应用于大鼠爪子时,溴芬酸(0.032-3.16%;100 μL)表现出剂量依赖性抗炎作用[3]。将溴芬酸(0.032-1.0%;50 μL)直接涂抹在豚鼠暴露于紫外线的皮肤区域,抑制红斑的效果比吲哚美辛高 26 倍 [3]。向大鼠未注射的爪子施用溴芬酸(0.0032-0.1%;50 μL)的剂量和持续时间都会导致后肢体积呈剂量和时间依赖性减少[3]。当向接受乙酰胆碱攻击的小鼠腹部局部给药时,溴芬酸(0.32%;50 μL)显着抑制腹部收缩[3]。在 4 周期间,溴芬酸(滴眼剂;每只眼睛 1 μL (0.09%);每天两次)会减慢并部分减少角膜染色 [4]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[2]
细胞类型:用转化生长因子-β2处理的人前囊 测试浓度: 80 μg/mL 孵育持续时间:48小时 实验结果:抑制转化生长因子-β2诱导的上皮-间质转化(LEC)。 细胞迁移测定[2] 细胞类型: HLEC-B3 细胞 测试浓度: 0、20、40、60 和80 μg/mL 孵育时间:24小时 实验结果:抑制转化生长因子-β2诱导的细胞迁移HLEC-B3 细胞,并表现出对上皮间质转化标志物过度表达的抑制。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male SD (SD (Sprague-Dawley)) rats (150-250 g) injected with carrageenan [3]
Doses: 0.0032, 0.01, 0.032, 0.1, 0.32, 1.0, 3.16% (100 or 200 μL) Route of Administration: 1 Carrageenan injected on back - 72 hrs (hrs (hours)) before injection Experimental Results: Significant anti-inflammatory activity was produced when applied at 0.32% 1, 2 and 4 hrs (hrs (hours)) before carrageenan challenge. Carrageenan is effective when applied 1 or 4 hrs (hrs (hours)) before challenge, but not 0.2% when applied 24 hrs (hrs (hours)) (or more) before challenge. Animal/Disease Models: Male injected with Salin or BTX-B[4] Doses: 1 μL (0.09%) per eye Route of Administration: eye drops; 1 μL (0.09%) per eye; twice a day; 4-week Experimental Results: Corneal fluorescein staining scores improved 4 weeks after treatment. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The plasma concentration of bromfenac following ocular administration in humans is unknown. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Milk levels of bromfenac are likely to be low with the usual oral dosage, but milk levels have not been measured after higher injectable dosages. Use caution when using bromfenac in nursing mothers, especially with the injectable drug. Maternal use of bromfenac eye drops would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Tetsuo Kida, et al. Pharmacokinetics and efficacy of topically applied nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in retinochoroidal tissues in rabbits. PLoS One. 2014 May 5;9(5):e96481.
[2]. Xiaobo Zhang, et al. Drug-eluting intraocular lens with sustained bromfenac release for conquering posterior capsular opacification. Bioact Mater. 2021 Jul 23;9:343-357. [3]. Nolan JC, et, al. The topical anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of bromfenac in rodents. Agents Actions. 1988 Aug; 25(1-2): 77-85. [4]. Kaevalin Lekhanont, et al. Effects of topical anti-inflammatory agents in a botulinum toxin B-induced mouse model of keratoconjunctivitis sicca. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Feb;23(1):27-34. |
| 其他信息 |
Bromfenac is amfenac in which the the hydrogen at the 4 position of the benzoyl group is substituted by bromine. It is used for the management of ocular pain and treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction. It was withdrawn from the US market in 1998, following concerns over off-label abuse and hepatic failure. It has a role as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and a non-narcotic analgesic. It is a member of benzophenones, a substituted aniline, an aromatic amino acid and an organobromine compound. It is functionally related to an amfenac. It is a conjugate acid of a bromfenac(1-).
Bromfenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) for ophthalmic use. Ophthalmic NSAIDs are becoming a cornerstone for the management of ocular pain and inflammation. Their well-characterized anti-inflammatory activity, analgesic property, and established safety record have also made NSAIDs an important tool for optimizing surgical outcomes. Non-ophthalmic formulations of bromfenac were withdrawn in the US in 1998 due to cases of severe liver toxicity. Bromfenac is a Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug. The mechanism of action of bromfenac is as a Cyclooxygenase Inhibitor. Bromfenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities. Upon ophthalmic administration, bromfenac binds to and inhibits the activity of cyclooxygenase II (COX II), an enzyme which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins (PG). By inhibiting PG formation, bromfenac is able to inhibit PG-induced inflammation, thereby preventing vasodilation, leukocytosis, disruption of the blood-aqueous humor barrier, an increase in vascular permeability and an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP). See also: Bromfenac Sodium (has salt form); Bromfenac; prednisolone acetate (component of) ... View More ... Drug Indication For the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction. FDA Label Treatment of postoperative ocular inflammation following cataract extraction in adults. Mechanism of Action The mechanism of its action is thought to be due to its ability to block prostaglandin synthesis by inhibiting cyclooxygenase 1 and 2. Prostaglandins have been shown in many animal models to be mediators of certain kinds of intraocular inflammation. In studies performed in animal eyes, prostaglandins have been shown to produce disruption of the blood-aqueous humor barrier, vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, leukocytosis, and increased intraocular pressure. Pharmacodynamics Bromfenac ophthalmic solution is a sterile, topical, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) for ophthalmic use. |
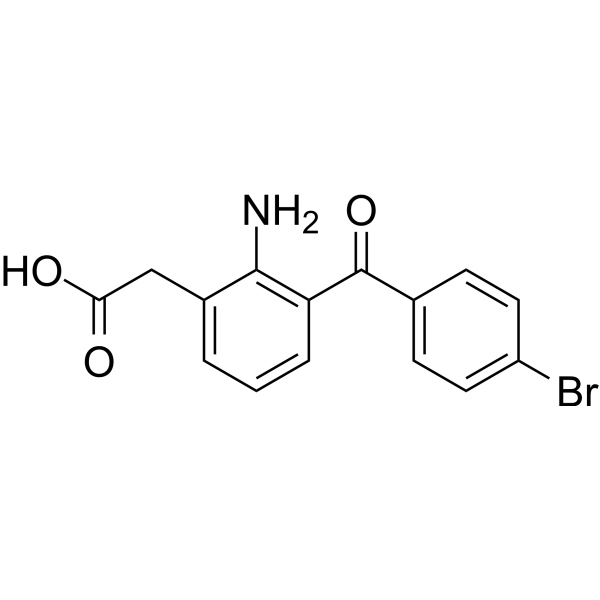
| 分子式 |
C15H12NO3BR
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
334.16468
|
| 精确质量 |
333
|
| CAS号 |
91714-94-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Bromfenac sodium;91714-93-1;Bromfenac sodium hydrate;120638-55-3
|
| PubChem CID |
60726
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
562.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
-129ºC
|
| 闪点 |
293.8±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.663
|
| LogP |
2.72
|
| tPSA |
80.39
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
366
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(CC1C(N)=C(C(C2C=CC(Br)=CC=2)=O)C=CC=1)O
|
| InChi Key |
ZBPLOVFIXSTCRZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H12BrNO3/c16-11-6-4-9(5-7-11)15(20)12-3-1-2-10(14(12)17)8-13(18)19/h1-7H,8,17H2,(H,18,19)
|
| 化学名 |
2-[2-amino-3-(4-bromobenzoyl)phenyl]acetic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9926 mL | 14.9629 mL | 29.9258 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5985 mL | 2.9926 mL | 5.9852 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2993 mL | 1.4963 mL | 2.9926 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。