| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
p97 ( IC50 = 9 nM )
The target of CB-5339 is Valosin-containing protein (VCP, also known as p97), an AAA+ ATPase. CB-5339 selectively inhibits the ATPase activity of VCP with an IC₅₀ value of ~13 nM. It exhibits high selectivity over other AAA+ ATPases (e.g., p97 homologs such as VCP-like protein 1, and other ATPases including Hsp70, Hsp90, and proteasomal ATPases), with IC₅₀ values against these off-targets being >10 μM. [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 AML 细胞中,CB-5339(0-1.6 μM;24-48 小时)会产生多聚泛素蛋白积累并触发未折叠蛋白反应 (UPR)[2]。
1. 对AML细胞系的抗增殖活性:CB-5339可强效抑制多种急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞系的增殖,IC₅₀值范围为~8 nM至~35 nM。例如,对FLT3-ITD突变型AML细胞系MOLM-13的IC₅₀约为10 nM,对MV4-11(FLT3-ITD突变型)的IC₅₀约为15 nM,对NPM1突变型OCI-AML3的IC₅₀约为22 nM,对MLL重排型THP-1的IC₅₀约为32 nM。相比之下,其对正常人造血祖细胞(CD34⁺细胞)的毒性显著较低,IC₅₀>1 μM。[2] 2. 诱导DNA损伤与凋亡反应:AML细胞经CB-5339(10-50 nM,处理24-48小时)处理后,DNA双链断裂积累,通过蛋白质印迹(western blot)检测显示DNA损伤标志物γH2AX水平升高;同时激活DNA损伤检查点通路,导致CHK2磷酸化(p-CHK2)和p53蛋白水平上调。此外,CB-5339可诱导AML细胞凋亡,流式细胞术(Annexin V/PI染色)结果显示,MOLM-13细胞经25 nM CB-5339处理48小时后,凋亡细胞(Annexin V⁺/PI⁻早期凋亡+Annexin V⁺/PI⁺晚期凋亡)比例约为45%,而溶剂对照组仅为~5%。这种凋亡效应与western blot检测到的促凋亡蛋白(如PUMA、BAX)上调及抗凋亡蛋白(如MCL-1)下调相关。[2] 3. 阻断VCP介导的蛋白质加工:CB-5339(10-50 nM)可抑制VCP依赖的错误折叠蛋白及DNA修复因子降解,导致泛素化蛋白积累(通过泛素蛋白western blot检测),并使DNA修复蛋白(如BRCA1、RAD51)滞留于细胞质中,无法进入细胞核发挥作用(通过免疫荧光染色评估)。[2] 4. 抑制克隆形成能力:CB-5339(5-20 nM)可显著降低AML细胞系及原代AML细胞的克隆形成能力。例如,10 nM CB-5339处理的MOLM-13细胞克隆形成数较溶剂对照组减少~90%,5例原代AML样本经15 nM处理后克隆数减少~75%。[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 MLL-AF9 驱动的患者来源异种移植 (PDX) AML 小鼠模型中,CB-5339(口服 90 mg/kg)可减少骨髓白血病浸润并延长小鼠的生存时间[2]。
1. 皮下AML异种移植模型中的抗肿瘤活性:对携带MOLM-13皮下肿瘤的NSG小鼠,给予CB-5339(10 mg/kg或20 mg/kg,口服灌胃,每日1次,每周5次,持续3周)。与溶剂对照组相比,10 mg/kg CB-5339可抑制~65%的肿瘤生长(第21天肿瘤体积:~200 mm³ vs. ~570 mm³),20 mg/kg可抑制~85%(第21天肿瘤体积:~80 mm³ vs. ~570 mm³)。肿瘤组织western blot分析显示γH2AX、p-CHK2及PUMA水平升高,证实体内VCP抑制及DNA损伤/凋亡诱导效应。[2] 2. 原位AML模型中的生存期延长:向NSG小鼠静脉注射MOLM-13细胞建立原位(骨髓来源)AML模型,给予CB-5339(15 mg/kg,口服灌胃,每日1次,每周5次)处理后,小鼠中位生存期显著延长:溶剂对照组生存期约28天,而CB-5339处理组约45天(风险比=0.22,p<0.001)。骨髓和脾脏的流式细胞术分析显示,CB-5339处理组小鼠的人CD45⁺(AML)细胞比例较溶剂组减少~70%。[2] 3. 原代AML患者来源异种移植(PDX)模型中的活性:向NSG小鼠静脉注射原代AML细胞(FLT3-ITD突变型),给予CB-5339(20 mg/kg,口服灌胃,每日1次,每周5次)处理4周后,骨髓中人CD45⁺细胞比例较溶剂组减少~68%;骨髓样本western blot检测显示γH2AX和泛素化蛋白水平升高,证实VCP抑制效应。[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
1. VCP ATP酶活性测定:使用重组全长人VCP蛋白(含N端结构域、D1和D2 ATP酶结构域),反应缓冲液含25 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.5)、5 mM MgCl₂、1 mM DTT、0.1 mg/mL BSA及1 mM ATP。将CB-5339进行系列稀释(0.1 nM至10 μM),与VCP(0.5 μM)在37°C预孵育30分钟;加入ATP启动反应,37°C孵育2小时后,采用发光ADP检测试剂盒检测ATP水解产生的ADP量,通过四参数逻辑模型计算IC₅₀。[2]
2. 对其他ATP酶的选择性测定:针对其他AAA+ ATP酶(如VCPL1、仅含D1结构域的p97、仅含D2结构域的p97)及非AAA+ ATP酶(如Hsp70、Hsp90、20S蛋白酶体),采用上述相同的ATP酶测定方案,使用各靶点特异性重组蛋白。CB-5339测试浓度最高达10 μM,通过计算相对于溶剂对照组的抑制百分比评估选择性。[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
1. 细胞活力测定:AML细胞系(MOLM-13、MV4-11等)以5×10³细胞/孔的密度接种于96孔板,加入系列稀释(0.1 nM至1 μM)的CB-5339,37°C(5% CO₂)孵育72小时后,加入细胞活力试剂(如CCK-8),2小时后检测450 nm处吸光度,通过四参数逻辑模型计算IC₅₀。正常CD34⁺细胞采用相同方案,接种密度为1×10⁴细胞/孔,孵育96小时。[2]
2. 蛋白质印迹(western blot)分析:AML细胞经CB-5339(10-50 nM)处理24-48小时后,收集细胞并用PBS洗涤,加入含蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA裂解液裂解;采用BCA法测定蛋白浓度,取20-30 μg蛋白进行SDS-PAGE电泳,转印至PVDF膜,用5%脱脂牛奶封闭1小时(室温);加入一抗(如抗γH2AX、抗p-CHK2、抗PUMA、抗泛素、抗GAPDH)4°C孵育过夜,再加入辣根过氧化物酶标记的二抗室温孵育1小时;采用化学发光试剂盒检测信号,通过图像分析软件定量条带强度(以GAPDH为内参)。[2] 3. 凋亡测定(Annexin V/PI染色):MOLM-13或MV4-11细胞经CB-5339(10-50 nM)处理48小时后,收集细胞并用冷PBS洗涤,重悬于Annexin V结合缓冲液中;加入Annexin V-FITC和PI,室温避光孵育15分钟,通过流式细胞术分析凋亡细胞(Annexin V⁺/PI⁻和Annexin V⁺/PI⁺)比例,计算相对于溶剂对照组的凋亡率。[2] 4. 克隆形成测定:AML细胞经CB-5339(5-20 nM)处理24小时后,用PBS洗涤去除残留药物,以500-1000细胞/孔的密度接种于含甲基纤维素培养基的6孔板,37°C(5% CO₂)孵育14-21天;手动计数≥50个细胞的克隆,克隆形成效率计算为(处理组克隆数/溶剂组克隆数)×100%。[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal Model: Patient-derived xenograft (PDX) AML model in male C57BL/6 mice driven by MLL-AF9[2]
Dosage: 90 mg/kg Administration: oral gavage (p.o.) Result: Reduced leukemic cell infiltration and circulation in the bone marrow as a result. 1. Subcutaneous AML xenograft model: Female NSG mice (6-8 weeks old) were subcutaneously injected with 5×10⁶ MOLM-13 cells (suspended in 100 μL PBS + 50% Matrigel) into the right flank. When tumors reached a volume of ~100 mm³, mice were randomized into three groups (n=6/group): vehicle control, CB-5339 10 mg/kg, and CB-5339 20 mg/kg. CB-5339 was formulated in a vehicle consisting of 10% Cremophor EL, 10% DMSO, and 80% normal saline. Drug was administered via oral gavage once daily, 5 days/week for 3 weeks. Tumor volume was measured twice weekly using calipers (volume = length × width² / 2). At the end of treatment, mice were euthanized, tumors were excised, weighed, and frozen for western blot analysis. [2] 2. Orthotopic AML model: Female NSG mice (6-8 weeks old) were intravenously injected with 1×10⁶ MOLM-13 cells (suspended in 100 μL PBS) via the tail vein. Seven days after cell injection, mice were randomized into two groups (n=8/group): vehicle control and CB-5339 15 mg/kg. CB-5339 was formulated as described above and administered via oral gavage once daily, 5 days/week. Mice were monitored daily for signs of disease (e.g., weight loss, lethargy, hind limb paralysis), and survival was recorded. When mice reached endpoint criteria, bone marrow and spleen were harvested, and human CD45⁺ cells were quantified via flow cytometry. [2] 3. Primary AML PDX model: Primary AML cells (1×10⁷ cells, from a FLT3-ITD mutant patient sample) were intravenously injected into female NSG mice (6-8 weeks old). Four weeks after engraftment (confirmed by flow cytometry of peripheral blood human CD45⁺ cells), mice were randomized into two groups (n=5/group): vehicle control and CB-5339 20 mg/kg. CB-5339 was administered via oral gavage once daily, 5 days/week for 4 weeks. At the end of treatment, bone marrow was harvested, human CD45⁺ cells were quantified via flow cytometry, and bone marrow lysates were analyzed by western blot for γH2AX and ubiquitin. [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Oral bioavailability: In CD-1 mice, CB-5339 was administered via intravenous (IV) injection (5 mg/kg) or oral gavage (10 mg/kg). Plasma samples were collected at 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 hours post-dose. Drug concentration in plasma was measured using LC-MS/MS. The oral bioavailability was calculated as (AUC₀→∞, oral × dose IV) / (AUC₀→∞, IV × dose oral) × 100%, resulting in a bioavailability of ~35%. [2]
2. Plasma pharmacokinetics (PK): After IV administration of 5 mg/kg CB-5339 to CD-1 mice, the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) was ~1200 ng/mL, the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC₀→∞) was ~1500 ng·h/mL, and the elimination half-life (t₁/₂) was ~4.2 hours. After oral administration of 10 mg/kg, Cmax was ~380 ng/mL (reached at ~1.5 hours post-dose), AUC₀→∞ was ~1050 ng·h/mL, and t₁/₂ was ~5.1 hours. [2] 3. Tissue distribution: In mice treated with oral CB-5339 (10 mg/kg), tissue samples (tumor, liver, kidney, spleen, bone marrow) were collected at 2 hours post-dose. CB-5339 concentrations were measured via LC-MS/MS. Tumor concentration was ~250 ng/g, which was ~6.6-fold higher than plasma concentration (~38 ng/mL) at the same time point. Liver and kidney concentrations were ~850 ng/g and ~420 ng/g, respectively, while spleen and bone marrow concentrations were ~310 ng/g and ~280 ng/g, respectively. [2] 4. Metabolism: In human liver microsomes, CB-5339 was metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 and CYP2C9. Incubation with recombinant CYP3A4 or CYP2C9 resulted in >50% metabolism of CB-5339 after 1 hour, while other CYP isoforms (e.g., CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2E1) showed <10% metabolism. The major metabolite was identified as a monohydroxylated derivative via LC-MS/MS. [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute and repeat-dose toxicity in mice: CD-1 mice were treated with CB-5339 at doses up to 40 mg/kg (oral gavage, once daily for 28 days). No mortality was observed at any dose. The only treatment-related effect was mild, reversible weight loss (~5-8%) at 30 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg during the first week of treatment, which recovered by the end of the study. Serum chemistry analysis showed no significant changes in liver function markers (ALT, AST) or kidney function markers (BUN, creatinine) compared to vehicle control. Hematology analysis showed no significant differences in white blood cell count, red blood cell count, or platelet count. [2]
2. Plasma protein binding: In human plasma, CB-5339 showed high protein binding (~97%), as determined by equilibrium dialysis. Plasma samples were spiked with CB-5339 (100 nM), dialyzed against phosphate-buffered saline for 4 hours at 37°C, and drug concentrations in the plasma and dialysate were measured via LC-MS/MS. The percentage of protein-bound drug was calculated as [(concentration in plasma - concentration in dialysate) / concentration in plasma] × 100%. [2] 3. Organ toxicity in xenograft models: In NSG mice treated with CB-5339 (up to 20 mg/kg, oral, 3-4 weeks), histopathological analysis of major organs (liver, kidney, spleen, heart, lung) showed no significant lesions or inflammation. Immunohistochemistry of bone marrow showed no significant reduction in normal hematopoietic cells, consistent with in vitro data showing low toxicity to CD34⁺ cells. [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
1. Background and mechanism of action: CB-5339 is a second-generation, selective VCP/p97 inhibitor designed to overcome limitations of first-generation VCP inhibitors (e.g., poor selectivity, high toxicity). VCP/p97 is critical for AML cell survival by mediating the degradation of misfolded proteins and DNA repair factors. CB-5339 binds to the D2 ATPase domain of VCP, inhibiting its ATPase activity, which blocks VCP-dependent protein processing. This leads to accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins, persistent DNA damage (due to impaired DNA repair), and activation of the p53-PUMA apoptotic pathway, ultimately inducing AML cell death while sparing normal hematopoietic cells. [2]
2. Indication relevance: CB-5339 is being developed for the treatment of AML, particularly AML subtypes dependent on VCP-mediated DNA repair (e.g., FLT3-ITD mutant, NPM1 mutant, MLL-rearranged AML). Preclinical data show efficacy in AML cell lines, primary AML cells, and AML xenograft models, including PDX models derived from patients with relapsed/refractory AML, supporting its potential as a targeted therapy for AML. [2] |
| 分子式 |
C24H24N6O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
412.49
|
| 精确质量 |
412.2
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.88; H, 5.86; N, 20.37; O, 3.88
|
| CAS号 |
1863952-15-1
|
| PubChem CID |
122685543
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to yellow solid powder
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
625
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C1=C(C=CC=C1)CNC1NC(N2C(C)=CC3C(=CC=CC2=3)C(N)=O)=NC2C=1CCCN=2
|
| InChi Key |
XDHFSLWWYBVSLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H24N6O/c1-15-13-19-17(21(25)31)9-5-11-20(19)30(15)24-28-22-18(10-6-12-26-22)23(29-24)27-14-16-7-3-2-4-8-16/h2-5,7-9,11,13H,6,10,12,14H2,1H3,(H2,25,31)(H2,26,27,28,29)
|
| 化学名 |
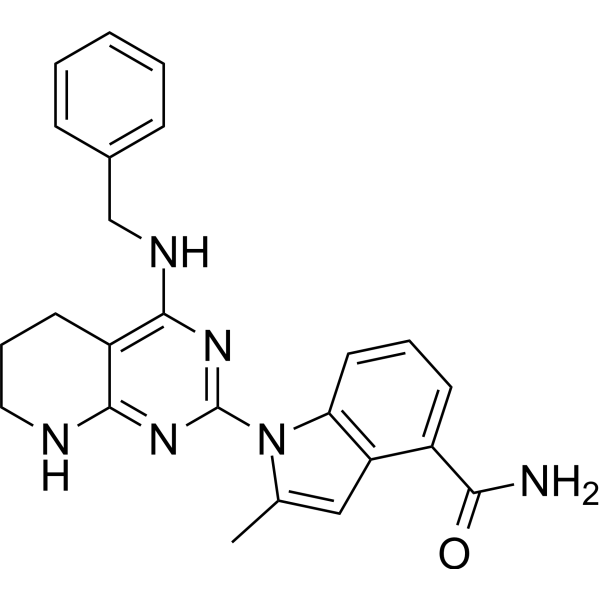
1-[4-(benzylamino)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-yl]-2-methylindole-4-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
CB-5339; CB5339; CB 5339; p97-IN-1; p97 IN 1
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL ( ~242.4 mM )
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4243 mL | 12.1215 mL | 24.2430 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4849 mL | 2.4243 mL | 4.8486 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2424 mL | 1.2122 mL | 2.4243 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04372641 | Withdrawn | Drug: p97 Inhibitor CB-5339 Tosylate | Aggressive Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma |
National Cancer Institute NCI |
June 18, 2020 | Phase 1 |
| NCT04402541 | Completed | Drug: CB-5339 | Acute Myeloid Leukemia, in Relapse Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
Cleave Therapeutics,Inc. | June 8, 2020 | Phase 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|