| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
GABAB receptor (IC50 = 85 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GABAB 受体拮抗剂 CGP52432 的 IC50 为 85 nM,分别比控制谷氨酸流出和生长抑素的受体低 35 倍和 100 倍 [1]。
如前所述,GABAB受体是异质的。大鼠大脑皮层轴突末端存在三种药理学上不同的受体亚型,分别介导γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)、谷氨酸或生长抑素释放的抑制。我们研究了上述受体亚型上的新型GABAB受体拮抗剂[3-[[(3,4-二氯苯基)甲基]氨基]丙基](二乙氧基甲基)次膦酸(CGP52432)。(-)-巴氯芬对K(+)诱发的大鼠皮质突触体释放GABA、谷氨酸或生长抑素的影响被CGP52432拮抗。该药物对GABA自身受体(0.085微M)的IC50分别比调节生长抑素和谷氨酸溢出的受体低35倍和100倍。在自身受体上,计算出的CGP52432的pA2为7.70,这使得该药物在该受体上的效力比phaclofen强约1000倍。CGP52432的效力和选择性特征表明,该药物是迄今为止研究大鼠大脑皮层末端GABAB自身受体的最合适工具[1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在高架十字迷宫中,CGP52432(10、30 mg/kg)对总头部倾斜或总手臂进入没有影响[2]。在大鼠中,当 CGP52432(100 nmol/kg,静脉注射或 1 nmol/kg,静脉注射)消除 GABA(50 μmol/kg,静脉注射)对缺血期间增强的肾交感神经活动 (RSNA) 的抑制作用时,GABA 的肾脏保护作用被消除[3]。
为此,我们从出生后第14-28天开始用选择性GABAB受体激动剂R-巴氯芬(2mg/kg,皮下注射)、GABAB接收器拮抗剂CGP52432(10mg/kg和30mg/kg)或赋形剂治疗雄性BALB/c小鼠幼崽(P)。然后在一系列行为测试中评估这些小鼠成年后(P62以后)的焦虑行为,包括:;应激诱导高温(SIH)试验、防御性大理石埋藏(DMB)、高架迷宫(EPM)和强迫游泳试验(FST)。产后R-巴氯芬治疗导致EPM中焦虑样行为增加,如回避和行为学测量所示。其他行为指标没有显著改变。有趣的是,在生命早期用CGP52432阻断GABAB受体不会导致情绪行为的改变。这些数据表明,在早期生活中,GABAB受体信号传导在成年后的焦虑行为编程中起着重要作用。这些影响背后的潜在神经发育过程仍有待发现。[2] 静脉注射荷包牡丹碱或CGP52432对GABA诱导的缺血性AKI改善的影响[3] 缺血前GABA治疗(50μmol/kg,静脉注射)显著抑制了缺血期RSNA的增强(图1a、b、d)。选择性GABAB受体拮抗剂CGP52432(10和100 nmol/kg,静脉注射)以剂量依赖的方式抑制了这种抑制作用(图1c,d)。相反,选择性GABAA受体拮抗剂荷包牡丹碱(1和10μmol/kg,静脉注射)治疗未能减弱GABA对RSNA的抑制作用(图1d)。 如图2所示,再灌注29小时后,缺血45分钟的大鼠肾功能明显恶化。与假手术大鼠相比,赋形剂治疗的AKI大鼠的血尿素氮(BUN)、血浆肌酐(PCr)浓度和尿流量(UF)显著增加,肌酐清除率(CCr)显著降低,表明肾功能障碍。向缺血性AKI大鼠静脉注射GABA(50μmol/kg)显著减轻了I/R诱导的肾功能障碍,这种改善被静脉注射100nmol/kg的CGP52432逆转。然而,GABA的肾脏保护作用不受荷包牡丹碱(1和10μmol/kg)或10 nmol/kg CGP52432的影响。此外,我们证实,单独静脉注射10μmol/kg的荷包牡丹碱对i/R诱导的肾损伤没有影响(数据未显示)。 组织学检查显示,再灌注29小时后,赋形剂治疗的AKI大鼠肾脏出现严重病变。与假手术大鼠的肾脏相比,这些变化的特征是内髓质小管中的蛋白质管型(图3b),内髓质条外区的髓质充血和出血(图3g),外髓质条外区管状坏死(图3l)(图3a、f、k)。向缺血性AKI大鼠静脉注射GABA可显著减轻所有病变的发展(表1;图3c,h,m)。此外,100 nmol/kgCGP52432(图3e,j,o)消除了这些GABA诱导的改善,而10μmol/kg,静脉注射,荷包牡丹碱对GABA的作用没有影响(图3d,i,n)。 静脉注射CGP52432对GABA诱导的缺血性AKI改善的影响[3] 如图4所示,0.1 nmol/kg静脉注射CGP52432可部分减弱GABA(50μmol/kg)对RSNA的抑制作用,而1 nmol/kg的静脉注射CGP52432几乎消除了GABA的作用。同样,0.1 nmol/kg静脉注射CGP52432可部分减弱GABA诱导的肾功能障碍改善,但1 nmol/kg的静脉注射CGP52432可几乎消除GABA诱导的改善(图5)。Bicuulline(10nmol/kg,i.c.v.)未能影响GABA诱导的肾脏保护作用(数据未显示)。 GABAB受体拮抗剂CGP52432(100 nmol/kg,静脉注射或1 nmol/kg的静脉注射)治疗消除了50μmol/kg,静脉内注射GABA对缺血期间增强的肾交感神经活动(RSNA)的抑制作用,从而消除了GABA的肾脏保护作用。侧脑室注射0.5μmol/kg GABA或静脉注射1μmol/kg巴氯芬(一种选择性GABAB受体激动剂)可预防i/R诱导的肾损伤,相当于静脉注射GABA。相反,静脉注射GABAA受体拮抗剂10μmol/kg荷包牡丹碱治疗,未能影响GABA对缺血性AKI的预防作用。因此,我们得出结论,中枢神经系统中的GABAB受体刺激,而不是外周GABAB接收器刺激,通过抑制肾缺血诱导的RSNA增强,介导了GABA对缺血性AKI的预防作用[3]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Two separate cohorts of male pups were used for the study. One cohort was treated with either R(+)baclofen HCl (2 mg/kg; Sigma; n = 10) or with vehicle (phosphate buffered saline, PBS; n = 13). The second cohort was treated with the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP52432 (10, 30 mg/kg; n = 10) or vehicle (PBS; n = 10). Drugs were freshly prepared for injection each day, by dissolution in PBS with vortexing and brief sonication. Doses of R(+)baclofen and CGP52432 were chosen based on those previously shown to be well tolerated in adult mice (Colombo et al., 2001, Voigt et al., 2011). All drug treatments were given via subcutaneous injection, once daily from P14-28 in a volume of 0.05 ml. This treatment regime was chosen as P14-28 has been demonstrated to be a period of vulnerability to the developmental effects of drugs acting on the GABAergic system [2].
Drugs or vehicle, except bicuculline and CGP52432, were injected 5 min before the start of ischaemia, whereas bicuculline and CGP52432 were administered 10 min before ischaemia to examine the effects of these drugs on GABA-induced renal protection. In sham-operated control rats, the left kidney was treated as above, but without clamping. Rats exposed to 45 min ischaemia were housed in metabolic cages for 24 h after reperfusion and 5 h urine samples were collected. At the end of urine collection, blood samples were drawn from the thoracic aorta and then the left kidney was excised under pentobarbital anaesthesia (50 mg/kg, i.p.). Plasma was isolated from the blood by centrifugation (1630 g, 15 min, 4°C) and used to measure renal function, as described below, whereas the kidneys were examined by light microscopy for histological analysis. CGP52432 was dissolved in saline (0.9%). [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
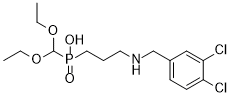
3-[(3,4-dichlorophenyl)methylamino]propyl-(diethoxymethyl)phosphinic acid is a dichlorobenzene.
Several mechanisms have been proposed for the effects of GABA in suppressing the peripheral sympathetic nervous system, including ganglionic blockade and/or inhibition of transmitter release from the nerve terminals.9, 23, 24 In the present study, we did not examine whether GABA suppressed NA overflow from peripheral sympathetic nerves because we did not use isolated tissues. Indeed, in the peripheral sympathetic nerves of AKI rats, systemically applied GABA may prevent I/R-induced renal injury by inhibiting NA release from nerve terminals, even after abrogating the GABA effect using CGP52432 However, the present study revealed that systemically applied GABA failed to prevent I/R-induced renal injury in rats administered i.c.v. CGP52432. These findings suggest that the renoprotective effect of GABA appears to be much more dependent on CNS neurotransmission than that mediated through peripheral sympathetic nerves. In conclusion, GABA suppressed the enhanced RSNA during ischaemia and increased NA overflow after I/R through activation of GABAB, but not GABAA, receptors and this effect was particularly focused on CNS activity rather than on peripheral nerve activity in the sympathetic nervous system. These inhibitory effects are presumably responsible for renoprotection against I/R-induced renal injury.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C15H24CL2NO4P
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
384.2351
|
| 精确质量 |
383.082
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 46.89; H, 6.30; Cl, 18.45; N, 3.65; O, 16.66; P, 8.06
|
| CAS号 |
139667-74-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
139667-74-6
|
| PubChem CID |
132252
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.258g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
544.4ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
283.1ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
1.1E-12mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.524
|
| LogP |
4.491
|
| tPSA |
77.6
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
369
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CCOC(OCC)P(=O)(CCCNCC1=CC(=C(C=C1)Cl)Cl)O
|
| InChi Key |
GJZVQXWEIYRHBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H24Cl2NO4P/c1-3-21-15(22-4-2)23(19,20)9-5-8-18-11-12-6-7-13(16)14(17)10-12/h6-7,10,15,18H,3-5,8-9,11H2,1-2H3,(H,19,20)
|
| 化学名 |
Phosphinic acid, (3-(((3,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl)amino)propyl)(diethoxymethyl)-
|
| 别名 |
Cgp 52432; Cgp52432;Cgp 52,432; Cgp-52,432; Phosphinic acid, P-[3-[[(3,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]amino]propyl]-P-(diethoxymethyl)-; 4ZH667RFW5; DTXSID20161147; Phosphinic acid, (3-(((3,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl)amino)propyl)(diethoxymethyl)-; (3-(((3,4-Dichlorophenyl)methyl)amino)propyl)(diethoxymethyl) phosphinic acid; ...; 139667-74-6; Cgp-52432.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~5 mg/mL (~13.01 mM)
H2O : ~4 mg/mL (~10.41 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6025 mL | 13.0127 mL | 26.0254 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5205 mL | 2.6025 mL | 5.2051 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2603 mL | 1.3013 mL | 2.6025 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。