| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
utrophin (EC50 = 0.91 μM); CYP1 enzyme
Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) targets the utrophin (UTRN) gene expression regulatory pathway [1] Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) [2][3][4][5] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
ezutromid 可诱导人类肌肉细胞中 utropin RNA 水平升高。治疗三天后,用 Ezutromid 处理的人 DMD 细胞中的 utropin 蛋白水平在最佳浓度 0.3 uM 下增加了一倍。 Ezutromid 被认为是安全且耐受性良好的,因为血浆浓度足够高,可导致细胞内 utropin 浓度上升 50%。 Ezutromid 使 Utrn mRNA 水平提高 30%,使 UTRN 蛋白水平提高 2.0 倍[3][4][5]。
在C2C12小鼠肌母细胞中,Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(1-10 μM)可剂量依赖性上调utrophin mRNA表达(10 μM时最大升高2.8倍)和蛋白水平(10 μM时升高2.5倍),分别通过qPCR和Western blot检测;撤药后该效应可维持72小时[1] - 在杜氏肌营养不良症(DMD)患者来源的人骨骼肌细胞(HSkMC)中,Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(5 μM)处理后utrophin蛋白表达较溶媒对照组升高2.3倍,且对细胞活力无显著影响(MTT法检测)[5] - 在utrophin启动子-荧光素酶报告基因实验(转染UTRN启动子-荧光素酶质粒的HEK293细胞)中,Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(0.1-20 μM)可剂量依赖性增加荧光素酶活性(EC50 = 3.7 μM),表明其激活utrophin转录调控[1] - 用Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(10 μM)孵育mdx小鼠肌管细胞,伊文思蓝染料摄取量减少约40%(较溶媒组),证实肌膜完整性改善[3] - 人肝微粒体代谢研究:Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) 代谢生成两种主要的1,2-反式-二氢-1,2-二醇代谢产物(M1和M2),代谢清除率为12.4 μL/min/mg蛋白[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在这项研究中,研究人员描述了SMT C1100的体内活性;第一个口服生物可利用的小分子utrophin上调剂。每天一次服用SMT C1100可以减少肌营养不良蛋白缺乏的许多病理影响。治疗可减少病理,改善肌肉生理,提高整体力量,并在强制运动后抵抗疲劳的能力;目前推荐作为DMD人体试验关键结果指标的六分钟步行测试的替代品。[3]
结论和意义:本研究证明了使用体外筛选方法鉴定utrophin转录上调的药物的原理。鉴定出的最佳化合物SMT C1100在DMD模型中显示出显著的疾病改善作用。我们的数据保证在DMD患者的临床试验中对这种化合物进行全面评估。[3] 在mdx小鼠(DMD模型)中,口服给予Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(30 mg/kg/天、60 mg/kg/天或120 mg/kg/天,连续4周)可剂量依赖性上调骨骼肌中utrophin蛋白表达(腓肠肌:较溶媒组升高2.1倍、3.5倍、4.2倍;膈肌:升高1.8倍、2.9倍、3.8倍)[3] - 高剂量Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(120 mg/kg/天,连续4周)处理mdx小鼠,骨骼肌病理显著改善:肌纤维坏死面积减少约65%,炎症细胞浸润(CD45+细胞)减少约58%,中心核频率降低约42%(较溶媒组)[3] - mdx小鼠经Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(60 mg/kg/天,连续8周)治疗后功能改善:握力增加约30%,跑步耐力(转棒实验)提升约45%,血清肌酸激酶(CK,肌肉损伤标志物)水平降低约55%[3] - 在mdx小鼠中,口服Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(100 mg/kg/天,连续12周)对心脏utrophin表达无显著影响,但轻微改善心脏功能(左心室射血分数增加约8%)[5] - 健康志愿者I期临床药代动力学研究:单次口服Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(100 mg至1600 mg)后,血浆AUC0-∞和Cmax呈剂量依赖性增加[4] |
| 酶活实验 |
体外代谢产物鉴定[2]
在人肝微粒体(HLM)中研究Ezutromid(BMN-195,SMTC-1100)。在加入NADPH(终浓度=1 mM)以引发反应之前,将微粒体(终浓度0.5mg/mL)、0.1M pH 7.4的磷酸盐缓冲液和试验化合物(终底物浓度=3µM;终DMSO浓度=0.25%)在37°C下预孵育。最终培养体积为25µL。对每种受试化合物进行对照培养,其中加入0.1 M pH 7.4的磷酸盐缓冲液代替NADPH。每个物种都含有两种对照化合物。对每种测试化合物单独进行所有孵育。每种化合物孵育0、5、15、30和45分钟。对照(减去NADPH)仅孵育45分钟。在适当的时间点加入50µL含甲醇内标终止反应。将培养板在4°C下以2500 rpm离心20分钟,以沉淀蛋白质。 HTRF测定:utrophin定量[2] 使用人utrophin HTRF试剂盒。在这种情况下,使用两种不同的特异性抗体以夹心法检测utrophin,一种用Eu3+-Cryptate标记(供体),另一种用d2标记(受体)。当供体/受体对非常接近时,用光源(激光或闪光灯)激发供体会触发朝向受体的荧光共振能量转移(FRET),受体进而以特定波长(665nm)发出荧光。在两个不同波长(供体为620nm,受体为665nm)下测量HTRF发射,可以对数据进行比率测量,以校正分析成分和介质的井间变异性和信号淬灭。 utrophin启动子-荧光素酶实验:将HEK293细胞接种到96孔板中,转染UTRN启动子-荧光素酶报告质粒和海肾荧光素酶内参质粒。转染24小时后,加入系列稀释的Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(0.1-20 μM),继续培养24小时。使用双荧光素酶检测系统测定荧光素酶活性,计算相对荧光素酶活性(萤火虫荧光素酶/海肾荧光素酶)以评估utrophin启动子的转录激活作用[1] - 肝微粒体代谢实验:将人肝微粒体与Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(10 μM)和NADPH生成系统在37°C下孵育60分钟。加入冰浴乙腈终止反应,通过液相色谱-串联质谱(LC-MS/MS)分离并鉴定代谢产物[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
富营养素萤火虫荧光素酶报告基因检测[2]
用5000个H2K-mdx-utrnA-luc细胞接种白色平底96孔板。在10%CO2和33°C下24小时后,从DMSO中的10 mM溶液储备中向细胞中加入化合物,一式三份(最终DMSO浓度为0.3%)。将细胞再孵育24小时(10%CO2,33°C)。使用FLUOstar Optima平板读数器测量使用萤光素酶测定系统试剂后的相对发光读数。用最小二乘回归的四参数逻辑斯谛函数(Levenberg-Marquardt算法)拟合生物三重样本的平均值,以计算EC50值。 C2C12肌母细胞utrophin表达实验:将C2C12细胞以5×10⁴个细胞/孔接种到6孔板中,更换为分化培养基培养5天诱导分化为肌管。用Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(1-10 μM)处理细胞24-72小时。提取总RNA用于qPCR分析UTRN mRNA水平(GAPDH作为内参基因),细胞裂解液用于Western blot检测utrophin蛋白(α-微管蛋白作为内参)[1] - DMD患者来源HSkMC实验:将DMD患者来源的HSkMC接种到6孔板中培养至汇合。用Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(5 μM)处理细胞48小时。通过Western blot定量utrophin蛋白表达,MTT法(570 nm处测定吸光度)评估细胞活力[5] - 肌膜完整性实验:将mdx小鼠肌管细胞接种到24孔板中,用Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100)(10 μM)处理24小时。向培养基中加入伊文思蓝染料(0.5 mg/mL)孵育1小时。用PBS洗涤细胞后,测定荧光强度(激发波长620 nm,发射波长680 nm)以评估染料摄取量(反映肌膜损伤程度)[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), 0.1% Tween-20, 5% DMSO); 50 mg/kg/day; Oral gavage
MDX Mice Sedentary mice and drug treatment[3] Three week-old male mdx (C57BL/10ScSn-Dmdmdx/J) littermates were randomly split between 2 groups and treated with Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) (50 mg/kg) or vehicle only (phosphate buffered saline (PBS), 0.1% Tween-20, 5% DMSO) via daily i.p. injection for four weeks. At the end of the drug treatment period mice were sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation in accordance with Schedule I of the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986. C57BL/6 contractile properties were measured in EDL muscle dissected from eight week old untreated mice obtained at 4 week of age from Harlan (n = 5). All animal procedures were performed in accordance with UK Home Office regulations. In all other experiments described using the sedentary mdx mice dosing was by the oral gavage using a canula to deliver Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) or vehicle only on a daily basis for 28 days. At the end of this period the mice were sacrificed and muscle and blood samples were taken. Quantification of muscle and plasma levels of SMT C1100 was performed using CD1 mice. Exercised mice, treadmill running and drug treatment[3] A total of 24 mdx male mice of 4–5 weeks of age, and homogeneous for body weight, underwent a 30 min running regime on an horizontal treadmill at 12 m/min, twice a week (keeping a constant interval of 2–3 days between each trial), for 4–6 weeks, according to a standard protocol. Experimental groups were treated as follows: vehicle only (n = 7), Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) (50 mg/kg; n = 6), α-methyl prednisolone (PDN; 1 mg/kg; n = 5) and combination of Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) (50 mg/kg) and PDN (1 mg/kg) (n = 6). Age and gender-matched wild type C57/BL10ScSn) or non-exercised mdx mice were also used for specific experimental purposes, as indicated in the text. The dose of PDN has been chosen based on our previous studies. The treatment started one day before the beginning of the exercise protocol, and continued until the day of sacrifice. Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) and the combination of PDN+Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) were dissolved in 5% DMSO, 0.1% Tween-20 in PBS, whilst PDN was dissolved in sterile water. Drugs were formulated for i.p. injection so that the correct dose was administered in 0.1 ml/10 g. Body weight was assessed weekly, as was fore-limb force by means of a grip strength meter. An exercise resistance test, consisting of horizontal running for 5 min at 5 m/min, then increasing the speed of 1 m/min each minute, was performed on week 0 and after four and five weeks of treatment. The total distance run by each mouse until exhaustion was measured. At the end of the 5th week of exercise/treatment the ex vivo experiments were also started. To this aim mice were deeply anesthetized and sacrificed using 1.2 g/kg urethane (i.p.) in accordance with the Italian Guidelines for the use of laboratory animals, which conform with the European Community Directive published in 1986 (86/609/EEC). mdx mouse efficacy study: Male mdx mice (4-6 weeks old) were randomly divided into vehicle control and Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) 30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg, 120 mg/kg groups (n=8 per group). The drug was dissolved in 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.2% Tween 80 and administered by oral gavage once daily for 4-12 weeks. Skeletal muscle (gastrocnemius, quadriceps, diaphragm) and heart tissues were collected at the end of treatment for utrophin expression analysis (Western blot, immunohistochemistry) and histopathological examination. Grip strength (digital force gauge) and rotarod performance (accelerating speed from 4 to 40 rpm over 5 minutes) were measured every 2 weeks. Serum CK levels were quantified by colorimetric assay [3][5] - Mouse pharmacokinetic study: Male CD-1 mice (8-10 weeks old) were given a single oral dose of Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) (100 mg/kg) formulated in 0.5% methylcellulose. Blood samples were collected at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24 hours post-dosing. Plasma was separated by centrifugation, and drug concentrations were quantified by LC-MS/MS. Pharmacokinetic parameters (t1/2, Cmax, AUC0-24h) were calculated using non-compartmental analysis [4] - Human clinical phase I study: Healthy male volunteers (18-45 years old) were enrolled in single-dose (100 mg, 200 mg, 400 mg, 800 mg, 1200 mg, 1600 mg) and multiple-dose (400 mg, 800 mg, 1200 mg once daily for 14 days) cohorts. Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) was administered as oral tablets. Blood samples were collected at predefined time points for PK analysis (LC-MS/MS). Safety assessments included physical examinations, vital signs, clinical laboratory tests (hematology, biochemistry, urinalysis), and adverse event monitoring [4] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Oral bioavailability: In humans, oral administration of Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) (single dose 400 mg) resulted in an oral bioavailability of ~52% [4]
- Plasma half-life (t1/2): In humans, terminal t1/2 was 18.7 ± 3.2 hours (single dose 400 mg); in mice, t1/2 was 6.8 ± 1.1 hours (oral 100 mg/kg) [4] - Peak plasma concentration (Cmax): In humans, Cmax was 1.8 ± 0.4 μg/mL (100 mg), 3.5 ± 0.7 μg/mL (200 mg), 7.2 ± 1.3 μg/mL (400 mg), 13.8 ± 2.5 μg/mL (800 mg), 20.5 ± 3.8 μg/mL (1200 mg), 28.3 ± 4.6 μg/mL (1600 mg) after single oral doses [4] - AUC0-∞: In humans, AUC0-∞ was 27.6 ± 5.1 μg·h/mL (400 mg single dose); in mice, AUC0-24h was 45.2 ± 8.3 μg·h/mL (100 mg/kg oral) [4] - Volume of distribution (Vd/F): In humans, Vd/F was 112 ± 23 L (400 mg single dose) [4] - Clearance (CL/F): In humans, CL/F was 5.8 ± 1.2 L/h (400 mg single dose); in mouse liver microsomes, metabolic clearance was 12.4 μL/min/mg protein [2][4] - Metabolism: Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) is primarily metabolized via cytochrome P450-mediated epoxidation followed by hydrolysis to form 1,2-trans-dihydro-1,2-diol metabolites (M1 and M2), which account for ~60% of plasma metabolites in humans [2] - Absorption: In humans, Tmax was 3.5 ± 0.8 hours (single dose 400 mg), with dose-proportional absorption up to 1600 mg [4] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Plasma protein binding: Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) exhibited plasma protein binding of 91-93% in human plasma and 88-90% in mouse plasma (equilibrium dialysis) [4]
- Human tolerability (Phase I study): Single oral doses up to 1600 mg and multiple doses up to 1200 mg/day for 14 days were well-tolerated. Most common adverse events (AEs) were mild to moderate headache (18%), nausea (12%), and fatigue (10%); no dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) or serious AEs were reported [4] - Clinical laboratory safety: In Phase I study, no significant changes in hematological parameters (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets), liver function (ALT, AST, bilirubin), or kidney function (creatinine, BUN) were observed in treated volunteers [4] - Acute toxicity in mice: Single oral dose of Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) up to 2000 mg/kg did not cause mortality or overt toxicity (weight loss, lethargy) [4] - Chronic toxicity in mice: Repeated oral administration of Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) (120 mg/kg/day for 12 weeks) showed no significant histopathological changes in liver, kidney, heart, or skeletal muscle [5] - Drug-drug interaction: No significant inhibition or induction of major CYP450 isoforms (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4) by Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) (up to 10 μM) in human liver microsomes [4] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Ezutromid has been investigated for the treatment of Muscular Dystrophy, Duchenne.
Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) is a first-in-class small-molecule utrophin upregulator, belonging to the 2-arylbenzoxazole class, developed for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) [1][3] - The therapeutic mechanism of Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) involves upregulating utrophin expression in skeletal muscle, which functionally compensates for the lack of dystrophin (defective in DMD) by stabilizing the sarcolemma and reducing muscle damage [1][3][5] - Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) shows tissue selectivity for skeletal muscle, with minimal effects on utrophin expression in non-muscle tissues (liver, kidney, brain) [5] - Second-generation utrophin modulators based on Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) have been developed with improved oral bioavailability and utrophin upregulation potency, but Ezutromid remains a benchmark compound for DMD therapy [5] - Ezutromid (BMN-195, SMTC-1100) has completed Phase I clinical trials, demonstrating favorable safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic profiles, supporting further clinical development for DMD [4] |
| 分子式 |
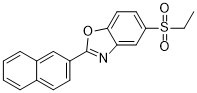
C19H15NO3S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
337.39
|
|
| 精确质量 |
337.077
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 67.64; H, 4.48; N, 4.15; O, 14.23; S, 9.50
|
|
| CAS号 |
945531-77-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
25109292
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
5.522
|
|
| tPSA |
68.55
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
543
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O=S(CC)(C1C=C2C(OC(C3C=C4C(C=CC=C4)=CC=3)=N2)=CC=1)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
KSGCNXAZROJSNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H15NO3S/c1-2-24(21,22)16-9-10-18-17(12-16)20-19(23-18)15-8-7-13-5-3-4-6-14(13)11-15/h3-12H,2H2,1H3
|
|
| 化学名 |
5-ethylsulfonyl-2-naphthalen-2-yl-1,3-benzoxazole
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9639 mL | 14.8196 mL | 29.6393 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5928 mL | 2.9639 mL | 5.9279 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2964 mL | 1.4820 mL | 2.9639 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 Effect of SMT C1100 onin vivoutrophin levels in themdxmouse.PLoS One.2011 May 6;6(5):e19189. |
|---|
 Ex vivoanalysis of SMT C1100 activity in themdxmouse.PLoS One.2011 May 6;6(5):e19189. |
 Effect of SMT C1100 onin vivoparameters of exercisedmdxmice.PLoS One.2011 May 6;6(5):e19189. |
 In vitroactivity of SMT C1100. |
|---|
 Effect of SMT C1100 treatment on calcium-dependent functional parameters of exercisedmdxmuscles.PLoS One.2011 May 6;6(5):e19189. |
 Reduction in secondary pathological features. Plasma levels of SMT C1100 in the mouse. |