| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
Endogenous Metabolite; alpha7 nicotinic receptors
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
甘油磷酸肌醇胆碱(0 或 70 μM,4 天)可以维持细胞活力并有效减少细胞凋亡 [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
甘油磷酸肌醇胆碱(皮下注射,0.2 和 100 mg/kg/h,24 或 48 小时)显着抑制巨噬细胞释放肿瘤坏死因子 (TNF),并减弱雌性 C57/Bl6 小鼠术后的伤害性反射。 2)[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定 [1]
细胞类型:大鼠嗜铬细胞瘤细胞 PC12 测试浓度: 0 或 70 μM 孵育时间: 4 天 实验结果: 70 μM 时细胞活力为 94%,0 μM 时细胞活力为 83%。与未处理组相比,70 μM 时显示 DNA 碎片(细胞凋亡特征)的细胞数量减少了 8.5%。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Female C57/Bl6 mouse postoperative pain model [2]
Doses: 0.2 and 100 mg/kg/h Route of Administration: subcutaneous injection, 24 or 48 hrs (hrs (hours)) Experimental Results: Thermal allergy was diminished after surgery and reached 48 hrs (hrs (hours)) after treatment For maximum efficacy, the ED50 value of the choline dose is 1.7 mg/kg/h. Allergic responses to punctate mechanical stimulation were diminished in a dose-dependent manner with an ED50 value of 4.7 mg/kg/h at 48 hrs (hrs (hours)) but not at 24 hrs (hrs (hours)) after infusion. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Treatment of rats with choline during critical periods in brain development results in long-lasting enhancement of spatial memory in their offspring. Apoptosis is a normal process during brain development, and, in some tissues, is modulated by the availability of the nutrient choline. In these studies, we examined whether availability of choline influences apoptosis in fetal brain and in the PC12 cell line derived from a rat pheochromocytoma. Timed-bred Sprague Dawley rats were fed a choline-deficient (CD), choline-control, or choline-supplemented (CS) diet for 6 days and, on embryonic day 18, fetal brain slices were prepared and apoptosis was assessed using terminal dUTP nucleotide end labeling (TUNEL) to detect DNA strand breaks and by counting of apoptotic bodies. TUNEL-positive cells were detected in 15.9% (P < 0.01), 8.7% and 7.2% of hippocampal cells from fetuses of dams fed the CD, control or CS diets, respectively. A similar inverse relationship between dietary intake of choline and TUNEL positive cells was detected in an area of cerebral cortex from these fetal brain slices. Counts of apoptotic bodies in fetal brain slices correlated inversely with choline intake of the mothers (6.2% (P < 0.01), 2.5% and 1.9% of hippocampal cells had apoptotic bodies in fetuses of dams fed the CD, control and CS diets, respectively). PC12 cells were grown in DMEM/F12 media supplemented with 70 microM choline or with 0 microM choline. The number of apoptotic bodies in PC12 cells increased when cells were grown in 0 microM choline medium (1.5%; P < 0.05) compared to 70 microM choline medium (0.55%). In PC12 cells, TUNEL labeling (DNA strand breaks) increased in choline deficient (13.5%, P < 0.05) compared to sufficient medium (5.0%). In addition, cleavage of genomic DNA-into 200 bp internucleosomal fragments was detected in choline-deficient cells. These results show that choline deficiency induces-apoptotic cell death in neuronal-type cells and in whole brain. We suggest that variations in choline availability to brain modulate apoptosis rates during development.[1]
Background: Choline is a dietary supplement that activates alpha7 nicotinic receptors. alpha7 nicotinic activation reduces cytokine production by macrophages and has antinociceptive activity in inflammatory pain models. We hypothesized that systemic administration of choline would reduce the inflammatory response from macrophages and have antinociceptive efficacy in a murine model of postoperative pain. Methods: We studied the response of wild-type and alpha7 nicotinic knockout mice to heat and punctate pressure after a model surgical procedure. We investigated the effect of genotype and choline treatment on alpha-bungarotoxin binding to, and their production of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) from, macrophages. Results: Choline provided moderate antinociception. The ED(50) for choline inhibition of heat-induced allodynia was 1.7 mg kg(-1) h(-1). The ED(50) for punctate pressure threshold was 4.7 mg kg(-1) h(-1) choline. alpha7 nicotinic knockout mice had no change in hypersensitivity to heat or pressure and were significantly different from littermate controls when treated with choline 5 mg kg(-1) h(-1) (P<0.05, 0.01). Choline 100 mM reduced binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to macrophages by 72% and decreased their release of TNF by up to 51 (sd 11)%. There was no difference by genotype in the inhibition of TNF release by choline. Conclusions: Systemic choline is a moderately effective analgesic via activation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. The antinocicepive effect may not be mediated by a reduction of TNF pathway cytokine release from macrophages. Although choline at millimolar concentrations clearly inhibits the release of TNF, this effect is not alpha7 subunit-dependent and occurs at concentrations likely higher than reached systemically in vivo.[2] |
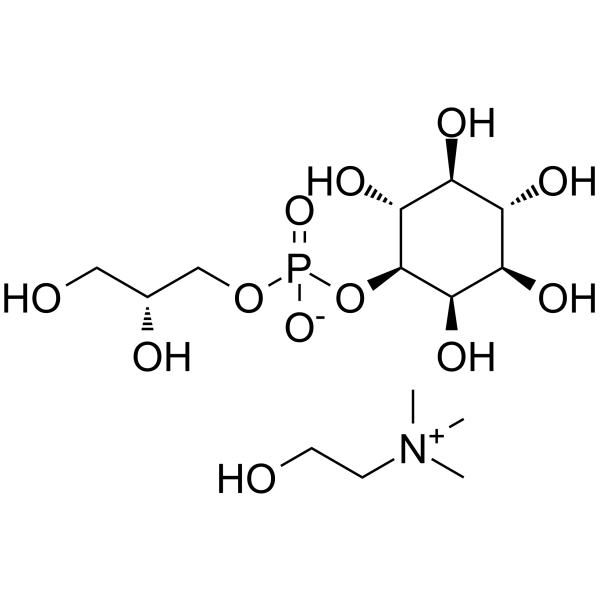
| 分子式 |
C14H32NO12P
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
437.37
|
| 精确质量 |
437.166
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 38.45; H, 7.37; N, 3.20; O, 43.90; P, 7.08
|
| CAS号 |
425642-32-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Choline chloride;67-48-1; Choline bitartrate;87-67-2;Choline Fenofibrate;856676-23-8;Choline-d4 chloride;285979-70-6;Choline-d9 chloride;61037-86-3;Choline Chloride-13C3;Choline theophyllinate;4499-40-5;Glycerophosphoinositol choline;425642-32-6;Choline-d6 chloride;Choline-d13 chloride;352438-97-2;Choline-13C2 chloride;202190-49-6; 425642-32-6 (choline); 129830-95-1 (free); 425642-29-1 (potassium); 425642-30-4 (sodium)
|
| PubChem CID |
91936944
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
220Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
8
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
401
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
| SMILES |
P(=O)([O-])(OC[C@@H](CO)O)OC1[C@@H]([C@H](C([C@H]([C@H]1O)O)O)O)O.OCC[N+](C)(C)C
|
| InChi Key |
PTZZCYHESHNXFL-SECXAADESA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H19O11P.C5H14NO/c10-1-3(11)2-19-21(17,18)20-9-7(15)5(13)4(12)6(14)8(9)16;1-6(2,3)4-5-7/h3-16H,1-2H2,(H,17,18);7H,4-5H2,1-3H3/q;+1/p-1/t3-,4?,5-,6+,7-,8-,9?;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
[(2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl] [(2R,3R,5S,6R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyl] phosphate;2-hydroxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium
|
| 别名 |
Plain; Glycerophosphoinositol choline; Glycerophosphoinositol choline; Plain; 425642-32-6; 3W4V4N5240; Glycerophosphoinositol (choline); UNII-3W4V4N5240; Glycerophosphoinositol choline [INCI]; D-Myo-inositol, 1-((2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl hydrogen phosphate), ION(1-), 2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium (1:1);
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2864 mL | 11.4320 mL | 22.8639 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4573 mL | 2.2864 mL | 4.5728 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2286 mL | 1.1432 mL | 2.2864 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。