| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在小鼠中,哌喹(10-90 mg/kg;单次腹腔注射)在所有测试剂量下均可降低寄生虫血症[1]。哌喹(90 mg/kg;单次腹腔注射)的t1/2、表观清除率和表观分布容积如下:17.8天、33.5 mg·h/L、1.55 L/h/kg和956 L/kg , 分别;健康小鼠为16.1天,疟疾小鼠为16.1天,分别为27.3 mg·h/L、1.9 L/h/kg和1,059 L/kg[1]。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Piperaquine is slowly absorbed and exhibits multiple peaks in its plasma concentration curve suggestive of enterohepatic recycling occurring alongside the absorption process. Due to this complication there is no discreet value for bioavailability but piperaquine is highly absorbed into systemic circulation. When taken with food, Cmax increases by 217% and mean exposure increases by 177%. Tmax is not affected by food and remains around 5 h. Piperaquine has been observed to accumulate more in females to a degree of 30-50% more than males. It also collects in red blood cells similar to [DB11638]. Piperaquine is mainly excreted in the feces with a negligible amount in the urine. Piperaquine is thought to distribute into a central compartment with an apparent volume of 26.7 L/kg, and two peripheral compartments with apparent volumes of 76.8 L/kg and 617 L/kg. These combine for a total volume of distribution of 720.5 L/kg. The mean apparent total clearance has been observed to be 1.12 L/h/kg in adult malaria patients. Metabolism / Metabolites Piperaquine undergoes N-dealkylation, separating its aliphatic bridge from one of the nitrogen-containing rings. The resulting aldehyde is then oxidized to a carboxylic acid to form metabolite 1 (M1). The same nitrogen-containing rings can also undergo hydroxylation at one of two sites to form M3 or M4. M2 is formed via N-oxidation of one of the nitrogens in the quinoline groups at either side of the molecule. M5 results when both of these nitrogens are oxidized. M1 and M2 are the major metabolism products. Each of these metabolites were observed in the urine. Biological Half-Life The terminal elimination half-life was observed to be 576h or 24 days. This is thought to be due to the extensive distribution of piperaquine. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Piperaquine's binding to plasma proteins is considered to be virtually complete. It has been measured to be >99% in humans, rats, and dogs. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Moore BR, et, al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of piperaquine in a murine malaria model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Jan; 52(1): 306-11.
[2]. Davis TME, et, al. Piperaquine: a resurgent antimalarial drug. Drugs. 2005; 65(1): 75-87. |
| 其他信息 |
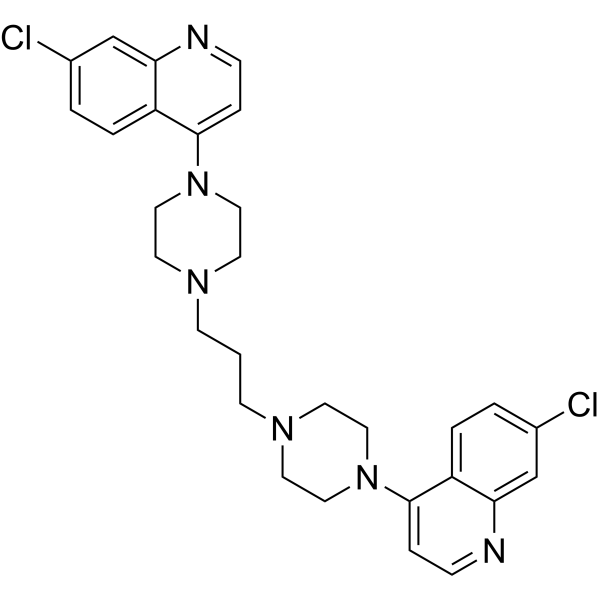
Piperaquine is an aminoquinoline that is 1,3-di(piperazin-1-yl)propane in which the nitrogen at position 4 of each of the piperazine moieties is replaced by a 7-chloroquinolin-4-yl group. It has a role as an antimalarial. It is a N-arylpiperazine, an organochlorine compound and an aminoquinoline.
Piperaquine is an antimalarial agent first synthesized in the 1960's and used throughout China. Its use declined in the 1980's as piperaquine resistant strains of *Plasmodium falciparum* appeared and artemisinin derivatives became available. It has come back into use in combination with the artemisinin derivative [DB11638] as part of the combination product Eurartesim. Eurartesim was first authorized for market by the European Medicines Agency in October 2011. Drug Indication For the treatment of uncomplicated *Plasmodium falciparum* infection in adults, children, and infants aged 6 months and up weighing over 5 kg. Used in combination with [DB11638]. FDA Label Mechanism of Action The mechanism of piperaquine inhibition of the haem detoxification pathway is unknown but is expected to be similar to that of [DB00608]. Pharmacodynamics Piperaquine inhibits the P. Falciparum parasite's haem detoxification pathway. |
| 分子式 |
C29H32CL2N6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
535.51
|
| 精确质量 |
534.206
|
| CAS号 |
4085-31-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Piperaquine phosphate;85547-56-4;Piperaquine tetraphosphate tetrahydrate;915967-82-7;Piperaquine tetraphosphate;911061-10-4;Piperaquine-d6;1261394-71-1
|
| PubChem CID |
122262
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
721.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
198-200°C (lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
389.9±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.664
|
| LogP |
5.15
|
| tPSA |
38.74
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
37
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
655
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C(CN1CCN(CC1)C2=CC=NC3=C2C=CC(=C3)Cl)CN4CCN(CC4)C5=CC=NC6=C5C=CC(=C6)Cl
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8674 mL | 9.3369 mL | 18.6738 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3735 mL | 1.8674 mL | 3.7348 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1867 mL | 0.9337 mL | 1.8674 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。