| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
Human Endogenous Metabolite; synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
促甲状腺激素 (TSH) 水平与脱碘酶 (DIO) 相关,脱碘酶可催化甲状腺素(激素原)转化为活性甲状腺激素。 DIO3 起到抑制甲状腺激素分泌的作用,而 DIO1 和 DIO2 则催化甲状腺激素分泌的激活。垂体TSH分泌的负反馈调节很大程度上依赖于DIO1和DIO2的活性[1]。已知离子通道、泵和调节性收缩蛋白的表达受三碘甲状腺原氨酸 (T3) 和左旋甲状腺素 (T4) 激素的调节。此外,已证明甲状腺激素影响负责兴奋和收缩的钙流动和稳态,L-甲状腺素和三碘甲状腺原氨酸影响该过程的药理调节和分泌。与喂养标准饮食的对照组相比,喂养无碘饮食 12 周的大鼠的 L-甲状腺素和三碘甲状腺原氨酸水平显着降低(p<0.001)。在接受低剂量药物治疗的组中,L-甲状腺素水平升高(p=0.02),但三碘甲状腺原氨酸水平基本上与对照组相同(p=0.19)。与未治疗的甲状腺功能减退组相比,给予大剂量 L-甲状腺素的大鼠显示三碘甲状腺原氨酸和 L-甲状腺素的循环浓度显着增加(分别为 p<0.001 和 p=0.004),并且L-甲状腺素水平相对于对照值 (p=0.03)[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
促甲状腺激素 (TSH) 水平与脱碘酶 (DIO) 催化甲状腺素(激素原)转化为活性甲状腺激素相关。甲状腺激素分泌由 DIO1 和 DIO2 激活,而分泌由 DIO3 灭活。负反馈对垂体TSH分泌的调节很大程度上依赖于DIO1和DIO2的作用[1]。离子通道、泵和调节收缩蛋白的表达受三碘甲状腺原氨酸 (T3) 和 L-甲状腺素 (T4) 激素的调节。此外,已证明甲状腺激素影响钙稳态和通量,负责兴奋和收缩。已知三碘甲状腺原氨酸和 L-甲状腺素可以改变钙的药理调节和分泌。与给予常规饮食的对照组相比,给予无碘饮食 12 周的大鼠的三碘甲状腺原氨酸和 L-甲状腺素水平显着降低(p<0.001)。三碘甲状腺原氨酸水平与对照组基本相当(p=0.19),但低剂量 L-甲状腺素治疗组中 L-甲状腺素有所增加(p=0.02)。与未治疗的甲状腺功能减退组相比,接受高剂量 L-甲状腺素治疗的大鼠表现出显着更高的三碘甲状腺原氨酸和 L-甲状腺素循环浓度(分别为 p<0.001 和 p=0.004),并且 L-甲状腺素水平显着高于对照组值(p=0.03)[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
生化技术[2] 根据制造商的方案,使用标准大鼠甲状腺素(T4)和T3 ELISA试剂盒进行ELISA测定。如前所述,进行了蛋白质印迹分析。
|
| 动物实验 |
Rats: The experiment uses 22 female Sprague-Dawley rats. There are four groups of non-pregnant rats: 1) No thyroid function, 2) hypothyroidism, 3) hypothyroidism treated with low doses of L-thyroxine (20 μg/kg/day), and 4) high doses of L-thyroxine (100 μg/kg/day). While the intervention rats (groups 2-4) are fed an iodine-free diet for 12 weeks to induce hypothyroidism, the control group (group 1) is fed a standard diet. This is followed by an additional 4 weeks of feeding to allow for L-thyroxine treatment and screening for hypothyroidism. You have unlimited access to food and water (iodine-free diet). Groups 3 and 4, which represent the hypothyroid group, receive intraperitoneal injections of 20 μg/kg and 100 μg/kg of L-thyroxine per day, respectively, every 24 hours. Within weeks 12 and 16 of starting the iodine-free or control diet, blood samples are taken for thyroid function screening. After treatment, a hysterectomy is performed under general anesthesia (isoflurane 2%), and the two uterine horns are kept in physiological Krebs' solution until isometric tension measurements are taken, which should take no longer than an hour.
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
bsorption is increased in the fasting state and decreased in malabsorption states (e.g., sprue); absorption also may decrease with age.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 3230
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for LEVOTHYROXINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Approximately 70% of secreted T4 is deiodinated to equal amounts of T3 and reverse triiodothyronine (rT3), which is calorigenically inactive. T4 is slowly eliminated through its major metabolic pathway to T3 via sequential deiodination, where approximately 80% of circulating T3 is derived from peripheral T4. The liver is the major site of degradation for both T4 and T3, with T4 deiodination also occurring at a number of additional sites, including the kidney and other tissues. Elimination of T4 and T3 involves hepatic conjugation to glucuronic and sulfuric acids. The hormones undergo enterohepatic circulation as conjugates are hydrolyzed in the intestine and reabsorbed. Conjugated compounds that reach the colon are hydrolyzed and eliminated as free compounds in the feces. Other minor T4 metabolites have been identified. Yields l-tyrosine in rabbit, in rat /From table/ Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. T-14 Yields 3,3',5-triiodo-L-thyronine in man, rat, dog, rabbit. /From table/ Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. T-14 Yields l-thyroxine-4'-beta-d-glucuronide in dog, in man, in rat. Yields l-thyroxine-4'-sulfate in dog. /From table/ Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. T-14 Yields 3,3',5,5'-tetraiodothyropyruvic acid in rat. Yields l-thyronine in rat. /From table/ Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. T-14 Yields 3,3'-diiodo-l-thyronine in dog. Yields 3,3',5,5'-tetraiodothyroacetic acid in man, in rat. /From table/ Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. T-14 Biological Half-Life T4 half-life is 6 to 7 days. T3 half-life is 1 to 2 days. In dogs orally administered levothyroxine has relatively ... short elimination half life when compared to humans. ... The serum half life is approximately 12-16 hours. Plumb D.C. Veterinary Drug Handbook. 8th ed. (pocket). Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015., p. 842 The usual plasma half-lives of thyroxine and triiodothyronine are 6-7 days and approximately 1-2 days, respectively. The plasma half-lives of thyroxine and triiodothyronine are decreased in patients with hyperthyroidism and increased in those with hypothyroidism. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Levothyroxine (T4) is a normal component of human milk. Limited data on exogenous replacement doses of levothyroxine during breastfeeding indicate no adverse effects in infants. The American Thyroid Association recommends that subclinical and overt hypothyroidism should be treated with levothyroxine in lactating women seeking to breastfeed. Adequate levothyroxine treatment during lactation may normalize milk production in hypothyroid lactating mothers with low milk supply. Levothyroxine dosage requirement may be increased in the postpartum period compared to prepregnancy requirements in patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Effects of exogenous thyroid hormone administration to mothers on their infant have not been reported. One case of apparent mitigation of cretinism in hypothyroid infants by breastfeeding has been reported, but the amounts of thyroid hormones in milk are not optimal, and this result has been disputed. The thyroid hormone content of human milk from the mothers of very preterm infants appears not to be sufficient to affect the infants' thyroid status. The amounts of thyroid hormones in milk are apparently not sufficient to interfere with diagnosis of hypothyroidism. In a telephone follow-up study, 5 nursing mothers reported taking levothyroxine (dosage unspecified). The mothers reported no adverse reactions in their infants. One mother who had undergone a thyroidectomy was taking levothyroxine 100 mcg daily as well as calcium carbonate and calcitriol. Her breastfed infant was reportedly "thriving" at 3 months of age. A woman with propionic acidemia took levothyroxine 50 mcg daily as well as biotin, carnitine, and various amino acids while exclusively breastfeeding her infant for 2 months and nonexclusively for 10 months. At that time, the infant had normal growth and development. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Adequate thyroid hormone serum levels are required for normal lactation. Replacing deficient thyroid levels should improve milk production caused by hypothyroidism. Supraphysiologic doses would not be expected to further improve lactation. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Arici M, et al. Association between genetic polymorphism and levothyroxine bioavailability in hypothyroid patients. Endocr J. 2018 Mar 28;65(3):317-323.
[2]. Corriveau S, et al. Levothyroxine treatment generates an abnormal uterine contractility patterns in an in vitro animalmodel. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2015 Sep 9;2(4):144-149. |
| 其他信息 |
Levothyroxine Sodium is the sodium salt of levothyroxine, a synthetic levoisomer of thyroxine (T4) that is similar to the endogenous hormone produced by the thyroid gland. In peripheral tissues, levothyroxine is deiodinated by 5'-deiodinase to form triiodothyronine (T3). T3 enters the cell and binds to nuclear thyroid hormone receptors; the activated hormone-receptor complex in turn triggers gene expression and produces proteins required in the regulation of cellular respiration; thermogenesis; cellular growth and differentiation; and the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids. T3 also exhibits cardiostimulatory effects.
The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (MONOIODOTYROSINE) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (DIIODOTYROSINE) in the THYROGLOBULIN. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form TRIIODOTHYRONINE which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. |
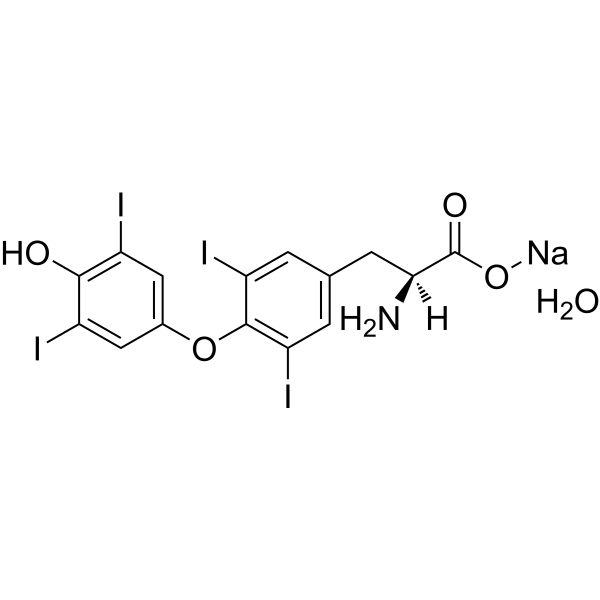
| 分子式 |
C15H12I4NNAO5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
816.87
|
| 精确质量 |
816.679
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 22.06; H, 1.48; I, 62.14; N, 1.71; Na, 2.81; O, 9.79
|
| CAS号 |
25416-65-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Thyroxine sulfate;77074-49-8;L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate;6106-07-6;L-Thyroxine sodium;55-03-8;L-Thyroxine-13C6-1;1217780-14-7;Biotin-(L-Thyroxine);149734-00-9;Biotin-hexanamide-(L-Thyroxine);2278192-78-0;Thyroxine hydrochloride-13C6;1421769-38-1;L-Thyroxine-13C6;720710-30-5;L-Thyroxine-13C6,15N;1431868-11-9
|
| PubChem CID |
23665037
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to light brown solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
576.3ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
207 °C
|
| 闪点 |
302.3ºC
|
| LogP |
3.922
|
| tPSA |
95.61
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
7
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
426
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
C1=C(C=C(C(=C1I)OC2=CC(=C(C(=C2)I)O)I)I)C[C@@H](C(=O)[O-])N.O.O.O.O.O.[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
JMHCCAYJTTWMCX-QWPJCUCISA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H11I4NO4.Na.5H2O/c16-8-4-7(5-9(17)13(8)21)24-14-10(18)1-6(2-11(14)19)3-12(20)15(22)23;;;;;;/h1-2,4-5,12,21H,3,20H2,(H,22,23);;5*1H2/q;+1;;;;;/p-1/t12-;;;;;;/m0....../s1
|
| 化学名 |
sodium;(2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoate;pentahydrate
|
| 别名 |
25416-65-3; Levothyroxine sodium; Levothyroxine sodium monohydrate; L-Thyroxine sodium xhydrate; Levothyroxine sodium hydrate; L-Thyroxine sodium hydrate; Monosodium L-thyroxine hydrate; 31178-59-3;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2242 mL | 6.1209 mL | 12.2418 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2448 mL | 1.2242 mL | 2.4484 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1224 mL | 0.6121 mL | 1.2242 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。