| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HBsAg(IC50: 2.8 nM);HBeAg(IC50: 2.6 nM);HBV DNA(IC50: 3.2 nM); TENT; PAPD5 and PAPD7
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
除了抑制HBsAg表达的有效活性外,RG7834在HepaG2.2.15细胞中也显示出抑制HBV DNA产生的非常有效的活性,IC50<0.13 nM,而核苷制剂拉米夫定(3-TC)的IC50约为25 nM。[1]
在HBV感染的dHepaRG细胞中,RG7834在单个数字nM浓度下抑制HBsAg、HBeAg和HBV DNA,而RG7834的对映体(R)-64在高达1μM的浓度下对所有三种病毒标志物都没有显示出显著的抑制作用。核苷药物ETV在抑制HBV DNA产生方面显示出非常有效的活性,IC50=0.06nM,但对HBsAg和HBeAg没有活性。RG7834和ETV之间的不同抗病毒特性表明,与核苷药物相比,RG7834的MOA有差异。[1] 为了评估RG7834的抗病毒选择性,在15种不同的DNA和RNA病毒的小组中测试该化合物。RG7834对所有这些病毒的IC50均高于10μM,表明RG7834具有很高的抗HBV特异性。[1] 为了更好地了解MOA,我们尝试了不同的方法来识别DHQ化学系列的分子靶标。最后,非经典的聚(A)RNA聚合酶,包含PAP相关结构域的蛋白质5和7(PAPD5和PAPD7)被鉴定为DHQ化合物的蛋白质靶标。[1] RG7834 ((S)-(+)-64) 的 IC50 分别为 2.8、2.6 和 3.2 nM,是一种有效且高度选择性的口服生物可利用的 HBV 抑制剂,可有效抑制 dHepaRG 细胞中的 HBV DNA 和抗原(HBsAg 和 HBeAg) [1]. RG7834 不会抑制 CYP3A4、CYP2D6、CYP2C9 (IC50 >50 μM) 和 hERG 通道[1]。 RG7834诱导的HBV信使核糖核酸衰变具有两个催化阶段[2] RG7834抑制PAPD5/7的poly(A)聚合酶功能[2] RG7834诱导的HBV核糖核酸3′剪切发生在细胞核和细胞质中[2]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
感染 HBV 的人肝嵌合 uPA-SCID 小鼠表现出对 RG7834(4 mg/kg,每天两次,持续 21 天)的抗 HBV 功效[1]。
在小鼠中,RG7834(2、14.5 mg/kg、 po) 的半衰期为 4.9 小时,具有良好的口服生物利用度[1]。 以ETV为对照,在HBV感染的人肝嵌合uPA SCID小鼠中评估体内抗HBV疗效。在用4 mg/kg每日两次给药治疗21天后,RG7834显著降低了HBsAg和HBeAg,而ETV对这两种抗原的降低没有明显疗效。RG7834在4 mg/kg的治疗下也将血清HBV DNA降低了0.6 log10,ETV显示出更明显的HBV DNA降低(图3)。体内结果与体外观察一致,最近报道了详细的生物学结果[1]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
微粒体稳定性测定[1]
为了测定微粒体的稳定性,将微粒体与试验化合物在37°C的磷酸钾缓冲液(100 mM,pH 7.4)中预孵育10分钟。最终孵育混合物由0.5mg微粒体蛋白/mL肝微粒体、1mM NADP、3mM葡萄糖6-磷酸、3mM MgCl2和0.05mg/mL葡萄糖6-磷酸脱氢酶组成,总体积为400μL磷酸钾缓冲液(100mM,pH 7.4)。反应是通过添加NADPH再生系统来引发的。在不同的时间点(0、3、6、9、15和30分钟),取等分试样(50μL),用150μL含内标乙腈骤冷。沉淀和离心后,通过LC-MS/MS分析上清液。 血浆蛋白结合测定[1] 使用分子量截止膜为12–14 kDa的96孔微平衡透析装置测定未结合的化合物。地西泮作为阳性对照。汇集的小鼠和人血浆购自Biopredic。在2-5个试剂盒中测量化合物,初始总浓度为1μM,其中一个试剂盒化合物为阳性对照。通过测定阳性对照的未结合分数值来测试膜的完整性。将等体积的空白透析缓冲液(pH 7.4的Soerensen缓冲液)和含有物质的基质样品分别加载到受体和供体室中。然后密封HTD透析块,并在5%CO2环境下于37°C的培养箱中保存5小时。然后通过LC-MS/MS对药物浓度进行定量。 |
| 细胞实验 |
HBsAg检测[1]
将HepG2.2.15细胞以1.5×104个细胞/孔的速度一式两份接种到白色96孔板中。用DMSO中的化合物的3倍连续稀释系列处理细胞。所有孔中的最终DMSO浓度为1%,并且DMSO用作非药物对照。应用HBsAg化学发光免疫分析(CLIA)试剂盒半定量测定乙型肝炎病毒分泌抗原水平。对于检测,使用50μL/孔培养上清液,并按照制造商的说明进行程序。使用CellTiter Glo测定细胞毒性。使用E-WorkBook Suite生成剂量-反应曲线,并外推IC50和CC50值。IC50和CC50定义为化合物浓度(或条件培养基对数稀释度),在该浓度下,与无药物对照相比,HBsAg的诱导和细胞毒性分别降低50%。 HBV DNA检测[1] 该检测采用实时qPCR直接测量细胞外HBV DNA拷贝数。将HepG2.2.15细胞接种在96孔微量滴定板中。只有内部孔用于减少细胞培养过程中观察到的“边缘效应”,外部孔填充完整的培养基以帮助最大限度地减少样品蒸发。第二天,洗涤HepG2.2.15细胞,并用含有不同浓度的试验化合物的完整培养基(一式三份)代替培养基。3TC被用作阳性对照,而单独的培养基被添加到细胞中作为阴性对照。三天后,用含有适当稀释的药物的新鲜培养基代替培养基。首次给药试验化合物后6天,收集细胞培养上清液,用Pronase处理,然后用于实时qPCR/TaqMan测定以测定HBV DNA拷贝数。抗病毒活性是根据HBV DNA水平(IC50)的降低来计算的。 Caco-2含量测定[1] 该药物是用pH 7.4 HBSS中的10μM输入药物溶液制备的。对于顶端到基底外侧的方向,向Caco-2细胞的顶端侧添加200μL输入药物溶液,向基底外侧添加700μL pH 7.4 HBSS(1%DMSO)。对于从基底外侧到顶端侧的方向,向Caco-2细胞的基底外侧添加700μL输入药物溶液,向顶端侧添加200μL pH 7.4 HBSS(1%DMSO)。将平板在37°C、95%湿度条件下的5%CO2中孵育1小时。测定顶端侧和基外侧的药物量,并计算从A到B和从B到A方向的渗透性。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal Model: HBV-infected human liver chimeric uPA-SCID mice[1]
Dosage: 4 mg/kg Administration: Twice daily for 21 days Result:demonstrates good oral bioavailability[1]. reduced serum HBV DNA in mice by 0.6 log10 and lowered both HBsAg and HBeAg. Pharmacokinetic (PK) Analysis in Mice[1] Compound was evaluated in mice at iv 1 mg/kg, po 2 mg/kg, and po 14.5 mg/kg. Compound solutions were prepared by dissolving the solid in 5% DMSO, 40% PEG400, and 55% saline for the iv dose and 1% RC-591 in water for the oral dose. Blood samples were collected at predetermined times into sodium heparin containing tubes, and plasma was separated via centrifugation (4 °C, 8000 rpm, 6 min) and stored frozen at −80 °C pending bioanalysis. Liver samples in the po group were harvested immediately after the collection of blood. The liver samples were then rinsed with saline, dried with filter paper, and stored at −80 °C until bioanalysis. Compound concentrations in the plasma and liver samples were determined by LC–MS/MS. The data were analyzed using a noncompartmental module of WinNonlin Professional 5.2. This PK study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Roche Pharma Research and Early Development China. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
RG7834 was selected for further physicochemical and ADME characterization based on its favorable anti-HBV activity, cytotoxicity, solubility, and liver microsome stability. With favorable measured log D value of 1.28 and pKa value of 5.79 (acidic), RG7834 showed very good permeability with a Papp(A–B) of 12.8 × 10–6 cm s–1 and Papp ratio of 1.3 in Caco-2 assay. The unbound fractions of RG7834 in human and mouse plasma were determined to be 32.8% and 35.2%, respectively. The mouse single dose pharmacokinetics (SDPK) profile of RG7834 was evaluated in male BALB/C mice following intravenous (iv) and oral (po) administration. The results are summarized in Table 6. RG7834 had moderate plasma clearance (Cl) (41.9 mL min–1 kg–1) and good oral bioavailability (F) (62%) in mice. RG7834 also demonstrated satisfactory oral exposure and, particularly, good liver exposure, which was 4-fold higher than that in plasma. Although we did not have free liver drug concentration, the reasonably high total concentration of RG7834 in liver was considered as a desirable attribute for anti-HBV drugs because liver is the target organ in chronic HBV infections.
The cynomolgus monkey SDPK study of RG7834 was conducted subsequently, and it showed low plasma clearance (4.6 mL min–1 kg–1) following intravenous administration. RG7834 also showed good oral bioavailability (57%) with a half-life of 4.9 h following oral administration. [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Simultaneously, we also assessed the in vitro safety profile of RG7834. In the in vitro drug–drug interaction (DDI) assessment, RG7834 showed IC50 values of >50 μM against CYP3A4, CYP2D6, and CYP2C9. It had no time dependent inhibition (TDI) issue and no CYP induction issue. Moreover, RG7834 demonstrated an excellent in vitro toxicology profile, showing no inhibition of hERG channel, no flag for glutathione adduction (GSH), and clean in Ames assay (mutagenicity) and micronucleus test (MNT, clastogenicity). [1]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a serious public health burden, and current therapies cannot achieve satisfactory cure rate. There are high unmet medical needs of novel therapeutic agents with differentiated mechanism of action (MOA) from the current standard of care. RG7834, a compound from the dihydroquinolizinone (DHQ) chemical series, is a first-in-class highly selective and orally bioavailable HBV inhibitor which can reduce both viral antigens and viral DNA with a novel mechanism of action. Here we report the discovery of RG7834 from a phenotypic screening and the structure-activity relationship (SAR) of the DHQ chemical series. RG7834 can selectively inhibit HBV but not other DNA or RNA viruses in a virus panel screening. Both in vitro and in vivo profiles of RG7834 are described herein, and the data support further development of this compound as a chronic HBV therapy.[1]
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) mRNA metabolism is dependent upon host proteins PAPD5 and PAPD7 (PAPD5/7). PAPD5/7 are cellular, noncanonical, poly(A) polymerases (PAPs) whose main function is to oligoadenylate the 3' end of noncoding RNA (ncRNA) for exosome degradation. HBV seems to exploit these two ncRNA quality-control factors for viral mRNA stabilization, rather than degradation. RG7834 is a small-molecule compound that binds PAPD5/7 and inhibits HBV gene production in both tissue culture and animal study. We reported that RG7834 was able to destabilize multiple HBV mRNA species, ranging from the 3.5-kb pregenomic/precore mRNAs to the 2.4/2.1-kb hepatitis B virus surface protein (HBs) mRNAs, except for the smallest 0.7-kb X protein (HBx) mRNA. Compound-induced HBV mRNA destabilization was initiated by a shortening of the poly(A) tail, followed by an accelerated degradation process in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. In cells expressing HBV mRNA, both PAPD5/7 were found to be physically associated with the viral RNA, and the polyadenylating activities of PAPD5/7 were susceptible to RG7834 repression in a biochemical assay. Moreover, in PAPD5/7 double-knockout cells, viral transcripts with a regular length of the poly(A) sequence could be initially synthesized but became shortened in hours, suggesting that participation of PAPD5/7 in RNA 3' end processing, either during adenosine oligomerization or afterward, is crucial for RNA stabilization.[2] |
| 分子式 |
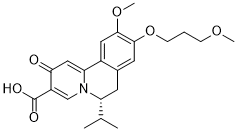
C22H27NO6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
401.452886819839
|
| 精确质量 |
401.18
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 65.82; H, 6.78; N, 3.49; O, 23.91
|
| CAS号 |
2072057-18-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
199482-36-3 (S-isomer hydrate);2072057-17-9 (S-isomer);2072057-18-0 (R-isomer);1802407-46-0 (racemic);
|
| PubChem CID |
118261819
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
| LogP |
3.8
|
| tPSA |
85.3Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
685
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
CC(C)[C@H]1CC2=CC(=C(C=C2C3=CC(=O)C(=CN13)C(=O)O)OC)OCCCOC
|
| InChi Key |
KBXLMOYQNDMHQT-QGZVFWFLSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H27NO6/c1-13(2)17-8-14-9-21(29-7-5-6-27-3)20(28-4)10-15(14)18-11-19(24)16(22(25)26)12-23(17)18/h9-13,17H,5-8H2,1-4H3,(H,25,26)/t17-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(6R)-6-Isopropyl-10-methoxy-9-(3-methoxypropoxy)-2-oxo-6,7-dihydrobenzo[a]quinolizine-3-carboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
RG7834 R-isomer; RG 7834 R-isomer; RG-7834 R-isomer; RO7020322 R-isomer; RO 7020322 R-isomer; RO-7020322 R-isomer; RO0321; RO-0321; RO 0321;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4910 mL | 12.4549 mL | 24.9097 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4982 mL | 2.4910 mL | 4.9819 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2491 mL | 1.2455 mL | 2.4910 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。