| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
PPARγ (Kd = 40 nM); PPARγ (EC50 = 60 nM); TRPC5 (EC50 = 30 μM); TRPM3
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
当暴露于罗格列酮钾 (0.1–10 μM) 72 小时时,多能 C3H10T1/2 干细胞会发生脂肪细胞发育 [1]。接触 1 μM 罗格列酮钾一小时会激活 PPARγ,后者与 NF-κ1 启动子结合并触发神经元基因转录 [3]。罗格列酮钾 (1 μM) 以 NF-κ1 依赖性方式上调 BCL-2 表达并保护 Neuro2A 细胞和海马神经元免受氧化应激 [3]。 TRPM3 抑制剂罗格列酮钾(0.01-100μM,15 分钟)对硝苯地平和 PregS 产生的活性的 IC50 值分别为 9.5 和 4.6μM [4]。罗格列酮钾(0.5-50 μM,7 天)可抑制卵巢癌细胞的增殖[7]。在 A2780 和 SKOV3 细胞中,罗格列酮钾(5 μM,7 天)可防止奥拉帕尼诱导的细胞衰老改变并刺激细胞凋亡 [7]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在糖尿病大鼠中,罗格列酮钾(5 mg/kg,每日)可降低血糖水平,持续八周[5]。通过激活 PPARγ 和 RXRα,罗格列酮钾(腹腔注射,3 mg/kg/天)可降低雄性 Wistar 大鼠 M1 巨噬细胞的极化,从而减轻香烟烟雾引起的气道炎症 [6]。在 A2780 和 SKOV3 小鼠皮下异种移植模型中,罗格列酮钾(腹腔注射,10 mg/kg,每 2 天)抑制皮下卵巢癌的生长 [7]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定 [7]
细胞类型: A2780 和 SKOV3 细胞 测试浓度: 0.5-50 μM 孵育时间:1-7天 实验结果:以时间依赖性和浓度依赖性的方式抑制细胞增殖。 蛋白质印迹分析[3] 细胞类型: 海马神经元 测试浓度: 1 μM 孵育时间:24小时 实验结果:NF-α1和BCL-2蛋白水平增加。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats [5]
Doses: 5 mg/kg Route of Administration: Orally, one time/day for 8 weeks. Experimental Results: The levels of IL-6, TNF-α and VCAM-1 were diminished in the diabetes group. Lipid peroxidation and nitrogen oxide levels were lower, while aortic glutathione and superoxide dismutase levels were increased compared with the diabetic group. Animal/Disease Models: Male Wistar rat [6] Doses: 3 mg/kg/day Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection, twice a day, 6 days a week, for 12 weeks Experimental Results: emphysema improved, PEF increased, total cells , increased neutrophil levels, and cigarette smoke (CS)-induced cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β). Inhibits CS-induced M1 macrophage polarization and reduces M1/M2 ratio. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Thiazolidinedione derivatives are antidiabetic agents that increase the insulin sensitivity of target tissues in animal models of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. In vitro, thiazolidinediones promote adipocyte differentiation of preadipocyte and mesenchymal stem cell lines; however, the molecular basis for this adipogenic effect has remained unclear. Here, we report that thiazolidinediones are potent and selective activators of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily recently shown to function in adipogenesis. The most potent of these agents, BRL49653, binds to PPAR gamma with a Kd of approximately 40 nM. Treatment of pluripotent C3H10T1/2 stem cells with BRL49653 results in efficient differentiation to adipocytes. These data are the first demonstration of a high affinity PPAR ligand and provide strong evidence that PPAR gamma is a molecular target for the adipogenic effects of thiazolidinediones. Furthermore, these data raise the intriguing possibility that PPAR gamma is a target for the therapeutic actions of this class of compounds.[1]
Diabetes with vascular complication needs strict interventions to retard possible serious complications. This research estimated the possible interaction of rosiglitazone (RGN) with losartan (Los) in diabetic rats. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into nondiabetic rats, diabetic rats, and diabetic rats that received RGN, Los, or a combination of RGN and Los. Measurement of serum glucose, vascular adhesion molecule-1, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, aortic lipid peroxide (malondialdehyde), glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and total nitrate/nitrite levels was done. Also, the effects of RGN on the relaxation created by acetylcholine and sodium nitroprusside, contraction of isolated aortic rings provoked by phenylephrine and angiotensin II were determined. Results revealed that RGN or Los had a vasodilating effect to variable degrees indicated by enhanced effects on both acetylcholine-induced relaxation and the antagonistic effect on angiotensin II and phenylephrine-stimulated contraction of diabetic aortas with significant amelioration in serum glucose, vascular adhesion molecule-1, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels and aortic oxidant/antioxidant balance. Treatment of diabetic rats with a combination of RGN and Los produced a more pronounced effect on the measured parameters compared to the diabetic, RGN-, and Los-treated groups. These findings point out the beneficial effects of RGN and Los combination in diabetic rats.[5] |
| 分子式 |
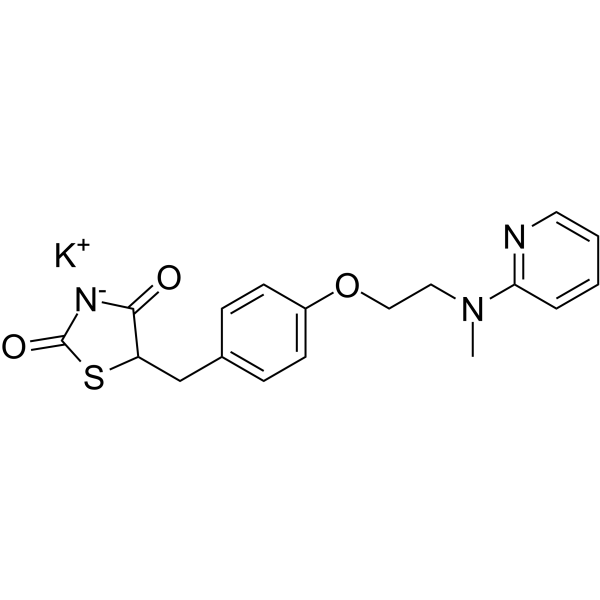
C18H18N3O3S-.K+
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
395.51712
|
| 精确质量 |
395.07
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 54.66; H, 4.59; K, 9.89; N, 10.62; O, 12.14; S, 8.11
|
| CAS号 |
316371-84-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Rosiglitazone;122320-73-4;Rosiglitazone hydrochloride;302543-62-0
|
| PubChem CID |
11463585
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| LogP |
2.605
|
| tPSA |
88.04
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
475
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CN(C1=CN=CC=C1)CCOC2=CC=C(CC3C(NC(S3)=O)=O)C=C2.[K]
|
| InChi Key |
RWOGCLSZSSKLEN-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H19N3O3S.K/c1-21(16-4-2-3-9-19-16)10-11-24-14-7-5-13(6-8-14)12-15-17(22)20-18(23)25-15;/h2-9,15H,10-12H2,1H3,(H,20,22,23);/q;+1/p-1
|
| 化学名 |
potassium;5-[[4-[2-[methyl(pyridin-2-yl)amino]ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidin-3-ide-2,4-dione
|
| 别名 |
Rosiglitazone (potassium salt); 316371-84-3; Rosiglitazone potassium; 2V3E7D3089; UNII-2V3E7D3089; potassium;5-[[4-[2-[methyl(pyridin-2-yl)amino]ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidin-3-ide-2,4-dione; 2,4-Thiazolidinedione, 5-((4-(2-(methyl-2-pyridinylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-, potassium salt; 2,4-Thiazolidinedione, 5-((4-(2-(methyl-2-pyridinylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-, potassium salt (1:1);
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5283 mL | 12.6416 mL | 25.2832 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5057 mL | 2.5283 mL | 5.0566 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2528 mL | 1.2642 mL | 2.5283 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。