| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
ROS; DNA topoisomerase; c-Jun; COX-2
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
小檗碱水合物(天然黄色18氯化物水合物;1.25-160 μM;72小时)可能对四种结直肠癌细胞系LoVo、HCT116、SW480和HT-29的生长有抑制作用[1]。小檗碱氯化物水合物(1.25-160 μM;24-72 小时)可促进 LoVo 细胞增殖的时间和剂量依赖性抑制 [1]。 LoVo 细胞用氯化小檗碱水合物 (10-80 μM) 处理 24 小时。通过流式细胞术对 40 μM 小檗碱处理的 LoVo 细胞进行细胞周期研究,结果显示细胞积累在 G2/M 期 [1]。小檗碱氯化物水合物 (10-80 μM) 在 24 小时后抑制细胞周期蛋白 B1、cdc2 和 cdc25c 蛋白表达,尤其是在 80.0 μM 剂量时 [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
人结直肠腺癌的体内生长受到氯化小檗碱水合物(天然黄色18氯化物水合物;10、30或50mg/kg/天;胃肠道灌胃;连续10天)的抑制。在裸鼠中,每天 30 毫克/公斤和 50 毫克/公斤的水合小檗碱可分别抑制人结直肠癌异种移植物 33.1% 和 45.3% [1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
蛋白质印迹和OPTDI分析用于检测细胞周期蛋白[1]
收获LoVo细胞,在100°C的裂解缓冲液[50 mmol/L TrisCl(pH 6.8)、100 mmol/L DTT、2%SDS、0.1%溴酚蓝、10%甘油]中裂解10分钟,并在−20°C下储存。蛋白质浓度通过BCA测定法测定。将等量的蛋白质装载到SDS聚丙烯酰胺凝胶上,并将蛋白质电泳转移到PVDF膜上。使用细胞周期蛋白B1、cdc2和cdc25c的特异性一级抗体(1:200稀释)分析免疫印迹,并与辣根过氧化物酶偶联的二级抗体(1:1000稀释)孵育,并使用增强化学发光检测试剂盒观察蛋白质。通过自动图像分析系统对光密度积分(OPTDI)进行分析。将细胞周期蛋白B1、cdc2和cdc25c的表达标准化为内部对照(GAPDH)。结果以处理与对照相比的百分比表示 DNA和蛋白质合成的测量[1] 通过3H-胸苷和L-[4,5-3H]-亮氨酸(分别为60 Ci/mg分子和0.5μCi/孔)的细胞掺入来评估DNA和蛋白质合成。将分离的细胞(每孔1×105个细胞)与含有一系列浓度的黄连素的培养基一起孵育。在24小时黄连素暴露前4小时,将放射性前体加入培养物中。在培养期结束时,将培养基移到一片滤膜上;用蒸馏水洗涤细胞三次。用液体闪烁光谱法测定3H-胸苷和L-[4,5-3H]-亮氨酸的掺入量。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞周期分析[1]
细胞类型: LoVo Cell 测试浓度: 0、10、20、40 或 80 μM 孵育持续时间:24 小时 实验结果:暴露于 40.0 μM 会诱导细胞周期停滞在 G2/M 期,并增加 G2/M 期群体和 G1 期相群逐渐减少。 蛋白质印迹分析[1] 细胞类型: LoVo Cell 测试浓度: 10、20、40 或 80 μM 孵育持续时间:24小时 实验结果:抑制cyclin B1、cdc2和cdc25c蛋白表达。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: 5weeks old BALB/c nu/nu (nude) mice with human colorectal adenocarcinoma LoVo xenografts [1]
Doses: 10, 30, or 50 mg/kg/day Route of Administration: Gastrointestinal gavage; continuous 10-day Experimental Results: At doses of 30 and 50 mg/kg/day, inhibition rates were 33.1% and 45.3%, respectively. In vivo anti-tumor effect of berberine in human colorectal adenocarcinoma (LoVo)[1] The in vivo antitumor efficacy of berberine was examined using human colorectal adenocarcinoma LoVo xenografts in a nude mouse model; 1 × 107 cells were implanted subcutaneous injection (s.c.) in the flanks of 5-week-old BALB/c nu/nu mice. After the tumors were grown up to about 1,000–1,500 mm3, the mice were sacrificed and the tumors were divided into equal fragments. Fragments (6–8 mm3) of colorectal adenocarcinoma were implanted s.c. in the flanks of 5-week-old BALB/c nu/nu mice. Tumors were allowed to develop for 2 weeks. Once tumors were established, the mice were divided randomly into five groups. The berberine-treated groups (ten mice each group) received 10, 30, or 50 mg kg−1 day−1 berberine by gastrointestinal gavage for 10 consecutive days. The 5-FU-treated group (10 mice) was given 30 mg kg−1 day−1 by intraperitoneal injection for 10 consecutive days. The control group (11 mice) was given sterile water. Measurements of body weights and tumor volumes were recorded every 1–3 days until the experimental endpoint, at which the tumors were debilitating to the mice. The long axis (L) and the short axis (S) were measured, and the tumor volume (V) was calculated using the following equation: V = S × S × L/2. Once the final measurement was taken, the mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The inhibitory rates were determined by comparing the volume of the control group and the treatment group: (1 − V treatment/Vcontrol). Effect of the combination of berberine and 5-FU on the growth of human colorectal adenocarcinoma (HT-29) xenografts in nude mice[1] The in vivo antitumor efficacy of the combination of berberine and 5-FU was examined using human colorectal adenocarcinoma HT-29 xenografts in a nude mouse model; 1 × 107 cells were implanted subcutaneous injection (s.c.) in the flanks of 5-week-old BALB/c nu/nu mice. After the tumors were grown up to about 1,000–1,500 mm3, the mice were sacrificed and the tumors were divided into equal fragments. Fragments (6–8 mm3) of colorectal adenocarcinoma were implanted s.c. in the flanks of 5-week-old BALB/c nu/nu mice. Tumors were allowed to develop for 3 weeks. Once tumors were established, the mice were divided randomly into four groups. The berberine-treated group (ten mice) received 50 mg kg−1 day−1 berberine by gastrointestinal gavage for 10 consecutive days. The 5-FU-treated group (10 mice) was given 30 mg kg−1 day−1 by intraperitoneal injection for 10 consecutive days. The combination group (10 mice) was given berberine and 5-FU. The control group (10 mice) was given sterile water. Measurements of body weights and tumor volumes were recorded every 3–4 days until the experimental endpoint, at which the tumors were debilitating to the mice. The long axis (L) and the short axis (S) were measured, and the tumor volume (V) was calculated using the following equation: V = S × S × L/2. Once the final measurement was taken, the mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The inhibitory rates were determined by comparing the volume of the control group and the treatment group: (1 − V treatment/V control). |
| 参考文献 |
| 分子式 |
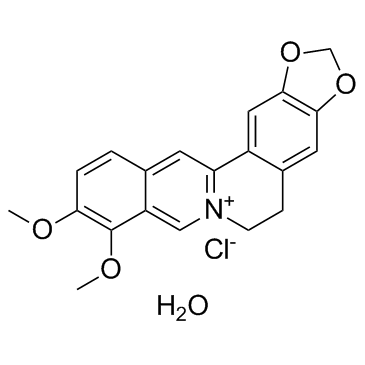
C20H20CLNO5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
389.8295
|
| 精确质量 |
389.103
|
| CAS号 |
68030-18-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Berberine chloride;633-65-8;Berberine;2086-83-1
|
| PubChem CID |
155074
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid
|
| 来源 |
Huanglian
|
| LogP |
3.834
|
| tPSA |
50.03
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
488
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
[Cl-].O1C([H])([H])OC2=C1C([H])=C1C(=C2[H])C2C([H])=C3C([H])=C([H])C(=C(C3=C([H])[N+]=2C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H].O([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
BPNJXFPOPCFZOC-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H18NO4.ClH.H2O/c1-22-17-4-3-12-7-16-14-9-19-18(24-11-25-19)8-13(14)5-6-21(16)10-15(12)20(17)23-2;;/h3-4,7-10H,5-6,11H2,1-2H3;1H;1H2/q+1;;/p-1
|
| 化学名 |
16,17-dimethoxy-5,7-dioxa-13-azoniapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,10.04,8.015,20]henicosa-1(13),2,4(8),9,14,16,18,20-octaene;chloride;hydrate
|
| 别名 |
Natural Yellow 18 chloride hydrate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 3.9 mg/mL (~10.00 mM)
H2O : ~1 mg/mL (~2.57 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5652 mL | 12.8261 mL | 25.6522 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5130 mL | 2.5652 mL | 5.1304 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2565 mL | 1.2826 mL | 2.5652 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。