| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
E3 Ligase
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
由于沙利度胺在有机相中的保留增加,(R)-沙利度胺从供体相到接收相的 R 印迹 MIP-1 转移显着减少。 (R)-沙利度胺对 MIP 引起的表面捕获的亲和力高于其他形式。我们发现 (R)-沙利度胺比其他药物更牢固地结合 MIP 选择性位点,这与这两种药物是不同的生物实体的事实相一致 [1]。与(R)-沙利度胺印迹MIP相比,(S)-沙利度胺印迹MIP纳米颗粒对caco-2细胞表现出更高的细胞毒性作用[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
成年雌性 F344 大鼠颅内、皮下(胁腹)或两者均植入 9L 胶质肉瘤肿瘤。单独口服沙利度胺和腹腔注射 BCNU 或顺铂联合化疗的疗效将在治疗几周后进行检查。 (R)-沙利度胺的血清和组织浓度均比 (S)-沙利度胺高 40-50%。 BCNU 或顺铂与沙利度胺共同给药不会改变浓度对映选择性 [1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Thalidomide is currently under evaluation as an anti-angiogenic agent in cancer treatment, alone and in combination with cytotoxic agents. Thalidomide is a racemate with known pharmacologic and pharmacokinetic enantioselectivity. In a previous study with thalidomide combination chemotherapy, we found evidence of anti-tumour synergy. In this study, we examined whether the synergy involved altered pharmacokinetics of thalidomide enantiomers. Adult female F344 rats were implanted with 9L gliosarcoma tumours intracranially, subcutaneously (flank), or both. Effectiveness of oral thalidomide alone, and with intraperitoneal BCNU or cisplatin combination chemotherapy, was assessed after several weeks treatment. Presumed pseudo steady-state serum, tumour and other tissues, collected after treatment, were assayed for R- and S-thalidomide by chiral HPLC. Both serum and tissue concentrations of R-thalidomide were 40-50% greater than those of S-thalidomide. Co-administration of BCNU or cisplatin with thalidomide did not alter the concentration enantioselectivity. Poor correlation of concentration with subcutaneous anti-tumour effect was found for individual treatments, and with all treatments for intracranial tumours. The consistency of the enantiomer concentration ratios across treatments strongly suggests that the favourable antitumour outcomes from interactions between thalidomide and the cytotoxic agents BCNU and cisplatin did not have altered enantioselectivity of thalidomide pharmacokinetics as their basis.[1]
Thalidomide, a racemate, is coming into clinical use as an immunomodulating and antiinflammatory drug. These effects may chiefly be exerted by S-thalidomide, but the enantiomers are interconverted in-vivo. Thalidomide is given orally, although parenteral administration would be desirable in some clinical situations. The aim of this study was to prepare solutions of the enantiomers of thalidomide for intravenous administration and to investigate their pharmacokinetics and sedative effects following infusion in man. Solubility and stability of the enantiomers in 5% glucose solution was investigated. After a dose-determination experiment in one subject, six healthy male volunteers received R- and S-thalidomide separately by 1-h infusions in a randomized double-blind cross-over study. Blood was sampled over 22h and sedative effects were recorded. Blood concentrations of the enantiomers were determined by stereospecific HPLC. A four-compartment model consisting of a two-compartment model for each enantiomer, with elimination from both compartments, connected by rate constants for chiral inversion was fitted to the concentration data, while the sedative effects were correlated with the blood concentrations of R- and S-thalidomide by means of logistic regression. The enantiomers of thalidomide were chemically stable in solution for at least a week at room temperature. The infusions were well tolerated. Sedation, which was the only observed effect, was related to the blood concentration of R-thalidomide. Inter-individual variation in the disposition of the enantiomers was modest (e.g. terminal half-lives ranged between 3.9 and 5.3h). Pharmacokinetic modelling predicted that varying the infusion time of a fixed dose of S-thalidomide between 10 min and 6h would have little influence on the maximal blood concentration of formed R-thalidomide. To our knowledge this is the first time that thalidomide has been administered intravenously.[2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
mouse LD50 oral 400 mg/kg BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY) Nature., 215(296), 1967 [PMID:6059519]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
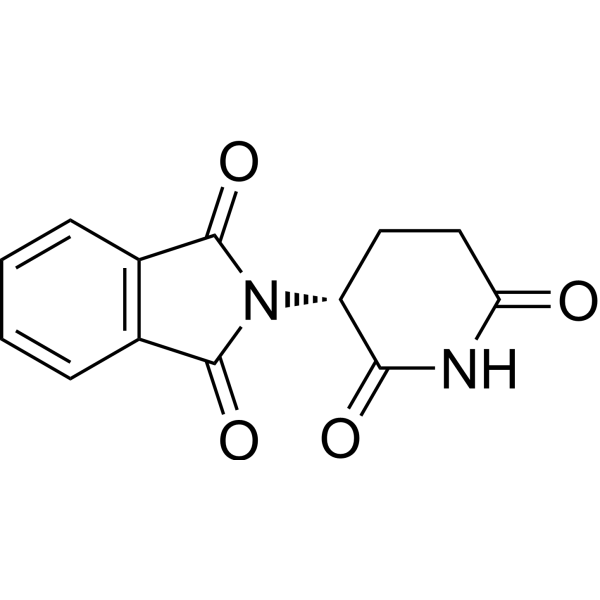
(R)-thalidomide is a 2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione that has R-configuration at the chiral centre. It has a role as a sedative. It is an enantiomer of a (S)-thalidomide.
See also: Thalidomide (annotation moved to). |
| 分子式 |
C13H10N2O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
258.2295
|
| 精确质量 |
258.064
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.47; H, 3.90; N, 10.85; O, 24.78
|
| CAS号 |
2614-06-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Thalidomide;50-35-1;(S)-Thalidomide;841-67-8;Thalidomide-d4;1219177-18-0
|
| PubChem CID |
75792
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.503g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
509.7ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
269-271ºC
|
| 闪点 |
262.1ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
1.65E-10mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.646
|
| LogP |
0.354
|
| tPSA |
83.55
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
19
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
449
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
C1CC(=O)NC(=O)[C@@H]1N2C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3C2=O
|
| InChi Key |
UEJJHQNACJXSKW-SECBINFHSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H10N2O4/c16-10-6-5-9(11(17)14-10)15-12(18)7-3-1-2-4-8(7)13(15)19/h1-4,9H,5-6H2,(H,14,16,17)/t9-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
2-[(3R)-2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl]isoindole-1,3-dione
|
| 别名 |
(R)-Thalidomide; (R)-(+)-thalidomide; (+)-Thalidomide; D-Thalidomide; 2614-06-4; R-(+)-Thalidomide; Thalidomide, (R)-; QN61H68KLK;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8725 mL | 19.3626 mL | 38.7252 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7745 mL | 3.8725 mL | 7.7450 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3873 mL | 1.9363 mL | 3.8725 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。