| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Dopamine D1/D5 receptor
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:SKF38393 (50-100 μM) 以蛋白质合成依赖性方式诱导持久的突触增强。在体外大鼠前额皮质神经元中,SKF 38393 模拟 DA 对 I(NaP) 的影响,并调节持续的钠电流。在听觉皮层中,SKF38393 通过激活下游效应器腺苷酸环化酶和磷脂酶 C 显着的蛋白质组改变来影响长期记忆的形成和巩固。激酶测定:SKF 38393 salthalide 是一种 D1 激动剂,IC50 为 110 nM。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
SKF 38393(6 mg/kg,腹腔注射)可防止东莨菪碱引起的 T 迷宫工作记忆任务表现受损。在成年雄性 NMRI 小鼠中,SKF38393(1 μg/小鼠)会损害情境依赖性恐惧学习。
多巴胺D(1)/D(5)受体激动剂可以通过模拟多巴胺对学习和记忆过程的神经生理学作用来增强认知。本研究考察了多巴胺D(1)/D(5)受体部分激动剂SKF-38393对大鼠认知效应的任务和性能依赖性。在T迷宫中评估了空间工作记忆,在水迷宫中评估空间参考记忆,在新环境(孔板)中评估了习惯学习。毒蕈碱乙酰胆碱受体拮抗剂东莨菪碱(1.5mg/kg,i.p.)用于损害这些学习任务的表现。单独给予SKF-38393(6mg/kg,i.p.)对T迷宫中的自发交替、逃到水迷宫中隐藏平台的潜伏期或孔板中自发行为的习惯化没有显著影响。相比之下,在东莨菪碱治疗的大鼠中,SKF 38393预防了东莨菪碱诱导的T迷宫缺陷,但加剧了水迷宫的损伤,并没有显著改变习惯化的破坏。这些结果表明,多巴胺D(1)/D(5)受体激活对认知功能具有性能和任务依赖性影响[2]。 |
||
| 酶活实验 |
使用定量放射自显影检查碘化SCH 23390、125I-SCH 23982(杜邦NEN)在大鼠脑切片中与多巴胺D1受体结合的效力、选择性以及解剖和神经元定位。125I-SCH 23982以非常高的亲和力(Kd值为55-125pM)、特异性(70-85%的结合被5微摩尔顺式氟戊噻醇取代)和可饱和的方式(Bmax值为65-176fmol/mg蛋白)结合基底节中的D1位点。选择性D1拮抗剂SCH 23390(IC50=90 pM)和顺式氟戊噻醇(IC50=200 pM)以及D1激动剂SKF 38393(IC50=110 nM)取代了特异性125I-SCH 23982结合,但D2选择性配体(I-舒必利,LY 171555)或S2拮抗剂西那塞林没有取代。与3H-SCH 23390相比,125I-SCH 23882对D1位点的亲和力提高了5到10倍,比放射性提高了50倍,使其成为标记D1受体的优秀放射性配体。D1位点的浓度在内侧黑质中最高,超过外侧黑质、尾壳核、伏隔核、嗅结节和内脚核中D1位点浓度的50%以上。较低浓度的D1位点存在于内囊、背内侧额叶皮层、屏状核和新皮层第6层。腹侧被盖区缺失D1位点。纹状体注射保留轴突的神经毒素喹啉酸,分别使同侧尾壳核和黑质内侧和中央网状部可移位D1位点的浓度减少87%和46-58%。黑质外侧未见D1位点丢失。用6-羟基多巴胺破坏高达94%的中脑多巴胺能投射并没有减少D1结合,也没有增加纹状体或黑质D1受体浓度,只有一个例外。125I-SCH 23982以皮摩尔亲和力选择性标记纹状体神经元上的D1结合位点,这些神经元包含大鼠大脑中的大部分D1位点[J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):213-222.]。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1995 Mar 28;92(7):2446-50;
[2]. Eur J Pharmacol.2007 Dec 22;577(1-3):71-7. |
||
| 其他信息 |
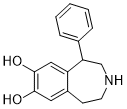
1-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine-7,8-diol is a benzazepine that is 2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-3-benzazepine bearing a phenyl substituent at position 1 and two hydroxy substituents at positions 7 and 8. It is a benzazepine, a member of catechols and a secondary amino compound.
A selective D1 dopamine receptor agonist used primarily as a research tool. Agonists of the dopamine D1/D5 receptors that are positively coupled to adenylyl cyclase specifically induce a slowly developing long-lasting potentiation of the field excitatory postsynaptic potential in the CA1 region of the hippocampus that lasts for > 6 hr. This potentiation is blocked by the specific D1/D5 receptor antagonist SCH 23390 and is occluded by the potentiation induced by cAMP agonists. An agonist of the D2 receptor, which is negatively coupled to adenylyl cyclase through G alpha i, did not induce potentiation. Although this slow D1/D5 agonist-induced potentiation is partially independent of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, it seems to share some steps with and is occluded by the late phase of long-term potentiation (LTP) produced by three repeated trains of nerve stimuli applied to the Schaffer collateral pathway. Similarly, the D1/D5 antagonist SCH 23390 attenuates the late phase of the LTP induced by repeated trains, and the D1/D5 agonist-induced potentiation is blocked by the protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin. These results suggest that the D1/D5 receptor may be involved in the late, protein synthesis-dependent component of LTP in the hippocampal CA1 region, either as an ancillary component or as a mediator directly contributing to the late phase. [1] The effects of SKF-38393 were clearly performance-dependent: SKF 38393-induced changes in learning were revealed in performance-impaired scopolamine-treated rats and were absent in control rats, which showed good performance of the tasks. However poor performance was not a predictor of a facilitatory effect on learning in all tasks. This contrasts with the performance-dependent effects of full dopamine D1/D5 receptor agonists in normal rats learning a variety of tasks, where poor performance at long delays was improved and good performance, at short delays, was impaired (Floresco et al., 2001, Chudasama and Robbins, 2004, Hotte et al., 2005). Our findings indicate that poor performance on a task seems insufficient on its own to reveal facilitatory effects of dopamine D1/D5 receptor activation on learning. An additional, task-dependent, effect of SKF-38393 on performance seems likely to be due to different levels of dopaminergic activity being needed for optimal learning of the different tasks (Chudasama and Robbins, 2004). Thus a fixed dose of a drug may lead to over-stimulation of dopamine D1/D5 receptors adversely affecting performance in some tasks and optimal receptor stimulation enhancing performance of other tasks. Even though a partial agonist like SKF 38393 would be expected to be less liable to cause over-stimulation of dopamine D1/D5 receptors than a full agonist, given the present findings, the use of partial agonists may not avoid detrimental effects on certain types of learning and memory at a dose that enhances others.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C16H17NO2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
255.32
|
|
| 精确质量 |
255.126
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 75.27; H, 6.71; N, 5.49; O, 12.53
|
|
| CAS号 |
67287-49-4
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
67287-49-4;62717-42-4 (HCl);81702-42-3 (R-isomer HCl);62751-59-1 (R-isomer); 20012-10-6 (HBr);
|
|
| PubChem CID |
1242
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
|
| 密度 |
1.209g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
467.1ºC at 760mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
180.1ºC
|
|
| LogP |
2.704
|
|
| tPSA |
52.49
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
19
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
291
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2CNCCC3=CC(=C(C=C32)O)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
JUDKOGFHZYMDMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H17NO2/c18-15-8-12-6-7-17-10-14(13(12)9-16(15)19)11-4-2-1-3-5-11/h1-5,8-9,14,17-19H,6-7,10H2
|
|
| 化学名 |
5-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine-7,8-diol
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9167 mL | 19.5833 mL | 39.1665 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7833 mL | 3.9167 mL | 7.8333 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3917 mL | 1.9583 mL | 3.9167 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28; 92(7): 2446–2450. |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28; 92(7): 2446–2450. |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28; 92(7): 2446–2450. |