| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在前列腺癌细胞系中,阿巴卡韦(15 和 150 μM,0-120 小时)单硫酸盐可抑制细胞增殖,修饰 LINE-1 mRNA 的表达,影响细胞周期的进展,并促进衰老[1]。阿巴卡韦单硫酸盐(15 和 150 μM,18 小时)可显着降低细胞迁移并防止细胞侵袭[1]。阿巴卡韦单硫酸盐诱导脂肪细胞凋亡[4]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
阿巴卡韦(0.7–7.5 μg/mL,100 μL,阴囊内注射;100 和 200 mg/kg,口服;4 小时)以剂量依赖性方式增加血栓形成[2]。在携带髓母细胞瘤的高危小鼠中,单硫酸阿巴卡韦(50 mg/kg/d;腹腔注射;14 天)联合 0.1 mg/kg/d 地西他滨可提高生存率[3]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定[1]
细胞类型: PC3、LNCaP 和 WI-38 测试浓度: 15 和 150 μM 孵育持续时间:0、24、48、72 和 96 小时 实验结果:证明对 PC3 和 LNCaP 具有剂量依赖性生长抑制作用。 细胞周期分析[1] 细胞类型: PC3 和 LNCaP 测试浓度: 150 μM 孵育持续时间:0、18、24、48、72、96和120小时 实验结果:导致PC3和LNCaP细胞中S期细胞的大量积累,并且在 PC3 细胞中观察到 G2/M 期增量。 细胞迁移测定 [1] 细胞类型: PC3 和 LNCaP 测试浓度: 15 和 150 μM 孵育时间: 18 小时 实验结果:细胞迁移显着减少。细胞侵袭测定[1] 细胞类型: PC3 和 LNCaP 测试浓度: 15 和 150 μM 孵育时间:18小时 实验结果:显着抑制细胞观察。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male mice (9-weeks old, 22-30 g) - wild-type (WT) C57BL/ 6 or homozygous knockout (P2rx7 KO, B6.129P2-P2rx7tm1Gab/J)[2]
Doses: 2.5, 5 and 7.5 μg/mL, 100 μL or 100 and 200 mg/kg Route of Administration: Intrascrotal or oral administration for 4 h Experimental Results: Dose-dependently promoted thrombus formation. Animal/Disease Models: NSGTM mice, patient-derived xenograft (PDX) cells of non-WNT/non-SHH, Group 3 and of SHH/ TP53-mutated medulloblastoma[3] Doses: 50 mg/kg/ d with 0.1 mg/kg/d Decitabine Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection, daily for 14 days Experimental Results: Inhibited tumor growth and enhanced mouse survival. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administration of a 600-mg dose of radiolabeled abacavir, 82.2% of the dose is excreted in urine and 16% of the dose is excreted in feces. The 5-carboxylic acid metabolite, 5-glucuronide metabolite, and unchanged abacavir accounted for 30, 36, and 1.2%, respectively, of recovered radioactivity in urine; unidentified minor metabolites accounted for 15% of recovered radioactivity in urine. It is not known whether abacavir is distributed into human milk; the drug is distributed into milk in rats. Abacavir crosses the placenta in rats. The oral bioavailability of abacavir is high with or without food; the CSF-to-plasma AUC ratio is approximately 0.3. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ABACAVIR SULFATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Abacavir is partially metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase (to form the 5'-carboxylic acid) and glucuronidation (to form the 5'-glucuronide). The metabolic fate of abacavir has not been fully determined, but the drug is metabolized in the liver. Abacavir is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase to form the 5-carboxylic acid and by glucuronyltransferase to form the 5-glucuronide; these metabolites do not appear to have any antiviral activity. Any involvement of cytochrome p450 isoenzymes in the metabolism of abacavir is limited. Intracellularly, abacavir is phosphorylated to abacavir monophosphate by adenosine phosphotransferase; abacavir monophosphate is then converted to carbovir monophosphate in a reaction catalyzed by cytosolic enzymes and then to carbovir triphosphate by cellular kinases. Intracellular (host cell) conversion of abacavir to carbovir triphosphate is necessary for the antiviral activity of the drug. The in vitro intracellular half-life of carbovir triphosphate in CD4+ CEM cells is 3.3 hours. Biological Half-Life The in vitro intracellular half-life of carbovir triphosphate /SRP: a metabolite of abacavir sulfate,/ in CD4+ CEM cells is 3.3 hours. The plasma elimination half-life of abacavir following a single oral dose (given as abacavir sulfate) is about 1.5 hours. In HIV-infected children 3 months to 13 years of age who received 8 mg/kg of abacavir every 12 hours (given as an oral solution containing abacavir sulfate), steady-state plasma elimination half-life averaged 1.3 hours and was essentially the same as that reported after a single dose. Following oral administration of a single 300-mg dose of abacavir to an individual with renal failure (glomerular filtration rate less than 10 mL/minute) undergoing peritoneal dialysis, the plasma elimination half-life of the drug was 1.33 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Abacavir appears in breastmilk in small quantities. Very little information is available on the safety of its use during breastfeeding. Achieving and maintaining viral suppression with antiretroviral therapy decreases breastfeeding transmission risk to less than 1%, but not zero. Individuals with HIV who are on antiretroviral therapy with a sustained undetectable viral load and who choose to breastfeed should be supported in this decision. If a viral load is not suppressed, banked pasteurized donor milk or formula is recommended. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants An HIV-positive mother took a combination tablet containing dolutegravir 50 mg, abacavir sulfate 600 mg and lamivudine 300 mg (Triumeq) once daily. Her infant was exclusively breastfed for about 30 weeks and partially breastfed for about 20 weeks more. No obvious side effects were noted. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Gynecomastia has been reported among men receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Gynecomastia is unilateral initially, but progresses to bilateral in about half of cases. No alterations in serum prolactin were noted and spontaneous resolution usually occurred within one year, even with continuation of the regimen. Some case reports and in vitro studies have suggested that protease inhibitors might cause hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea in some male patients, although this has been disputed. The relevance of these findings to nursing mothers is not known. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Abacavir (brand name: Ziagen) is a prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of HIV infection in adults, children, and infants. Abacavir is always used in combination with other HIV medicines.
See also: Abacavir Sulfate (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Ziagen is indicated in antiretroviral combination therapy for the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection in adults, adolescents and children. The demonstration of the benefit of Ziagen is mainly based on results of studies performed with a twice daily regimen, in treatment-naïve adult patients on combination therapy. Before initiating treatment with abacavir, screening for carriage of the HLA-B*5701 allele should be performed in any HIV-infected patient, irrespective of racial origin. Abacavir should not be used in patients known to carry the HLA-B*5701 allele. Mechanism of Action Like dideoxynucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (e.g., didanosine, lamivudine, stavudine, zalcitabine, zidovudine), the antiviral activity of abacavir appears to depend on intracellular conversion of the drug to a 5-triphosphate metabolite; thus, carbovir triphosphate (carbocyclic guanosine triphosphate) and not unchanged abacavir appears to be the pharmacologically active form of the drug. Substantial differences exist in the rates at which human cells phosphorylate various nucleoside antiviral agents and in the enzymatic pathways involved. Enzymatic conversion of abacavir to carbovir triphosphate appears to be complex and involves certain steps and enzymes that differ from those involved in the enzymatic conversion of dideoxynucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Abacavir is phosphorylated by adenosine phosphotransferase to abacavir monophosphate, which is converted to carbovir monophosphate by a cytosolic enzyme. Subsequently, carbovir monophosphate is phosphorylated by cellular kinases to carbovir triphosphate. Abacavir is not a substrate for enzymes (i.e., thymidine kinase, deoxycytidine kinase, adenosine kinase, mitochondrial deoxyguanosine kinase) known to phosphorylate other nucleoside analogs. Because phosphorylation of abacavir depends on cellular rather than viral enzymes, conversion of the drug to the active triphosphate derivative occurs in both virus-infected and uninfected cells. Carbovir triphosphate is a structural analog of deoxyguanosine-5-triphosphate (dGTP), the usual substrate for viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase. Although other mechanisms may be involved in the antiretroviral activity of the drug, carbovir triphosphate appears to compete with deoxyguanosine-5-triphosphate for viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase and incorporation into viral DNA. Following incorporation of carbovir triphosphate into the viral DNA chain instead of deoxyguanosine-5-triphosphate, DNA synthesis is prematurely terminated because the absence of the 3-hydroxy group on the drug prevents further 5 to 3 phosphodiester linkages. The complete mechanism(s) of antiviral activity of abacavir has not been fully elucidated. Following conversion to a pharmacologically active metabolite, abacavir apparently inhibits replication of retroviruses, including human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and type 2 (HIV-2), by interfering with viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase). The drug, therefore, exerts a virustatic effect against retroviruses by acting as a reverse transcriptase inhibitor. |
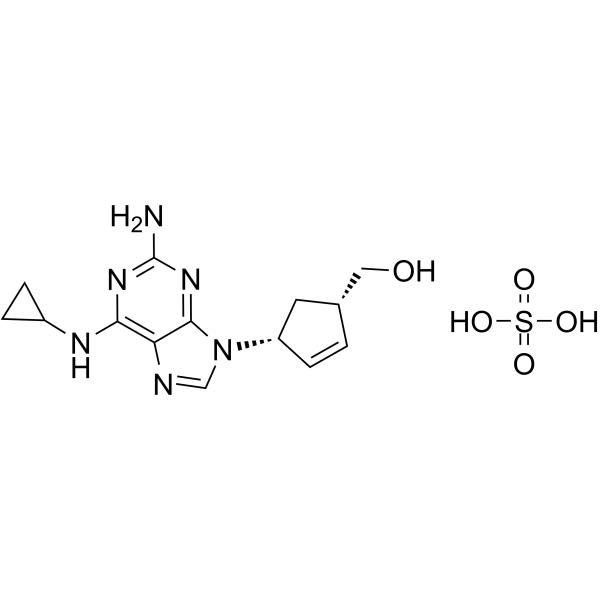
| 分子式 |
C14H20N6O5S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
384.410800933838
|
| 精确质量 |
384.121
|
| CAS号 |
216699-07-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Abacavir;136470-78-5;Abacavir sulfate;188062-50-2;Abacavir hydrochloride;136777-48-5
|
| PubChem CID |
9843042
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid
|
| tPSA |
185
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
496
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
S(O)(O)(=O)=O.N(C1CC1)C1N=C(N)N=C2N([C@H]3C=C[C@@H](CO)C3)C=NC=12
|
| InChi Key |
MBFKCGGQTYQTLR-SCYNACPDSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H18N6O.H2O4S/c15-14-18-12(17-9-2-3-9)11-13(19-14)20(7-16-11)10-4-1-8(5-10)6-21;1-5(2,3)4/h1,4,7-10,21H,2-3,5-6H2,(H3,15,17,18,19);(H2,1,2,3,4)/t8-,10+;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
[(1S,4R)-4-[2-amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)purin-9-yl]cyclopent-2-en-1-yl]methanol;sulfuric acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6014 mL | 13.0069 mL | 26.0139 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5203 mL | 2.6014 mL | 5.2028 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2601 mL | 1.3007 mL | 2.6014 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。