| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |

| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rapidly absorbed following both intramuscular and subcutaneous injection. Initial blood levels following parenteral administration are high but transient. Oral absorption in fasting, healthy humans is only about 15-30% as it is very susceptible to acid-catalyzed hydrolysis. Penicillin G is eliminated by the kidneys. Nonrenal clearance includes hepatic metabolism and, to a lesser extent, biliary excretion. 0.53–0.67 L/kg in adults with normal renal function 560ml/min in healthy humans ...WIDELY DISTRIBUTED THROUGHOUT BODY... ITS APPARENT VOL OF DISTRIBUTION IS IN ABOUT 50% OF TOTAL BODY WATER. MORE THAN 90%...IN BLOOD IS IN PLASMA & LESS THAN 10% IS IN ERYTHROCYTES; APPROX 65% IS REVERSIBLY BOUND TO PLASMA ALBUMIN. LOW CONCN OF PROTEIN...LOW DEGREE OF BINDING...DRUG EFFICACY. SIGNIFICANT AMT APPEAR IN LIVER, BILE, KIDNEY, SEMEN, LYMPH, & INTESTINE. ... PENICILLIN DOES NOT READILY ENTER CSF WHEN MENINGES ARE NORMAL. ORAL DOSES OF 500 MG POTASSIUM PENICILLIN G TO HUMAN SUBJECTS RESULT IN URINARY CONCN OF 600 UG/ML, FOR 2 HR, & 300 UG/ML, FOR 4 HR AFTER DOSING. ... INEFFICIENT PLACENTAL TRANSFER IS CONSISTENT WITH LOW LIPID SOLUBILITY & LOW IONIZATION CONSTANT OF PENICILLIN G & THERE IS NO EVIDENCE OF PLACENTAL TRANSPORT. ...RAPIDLY ELIMINATED FROM BODY, MAINLY BY KIDNEY BUT IN SMALL PART IN BILE & BY OTHER CHANNELS. ... CLEARANCE VALUES ARE CONSIDERABLY LOWER IN NEONATES & INFANTS, BECAUSE OF INCOMPLETE DEVELOPMENT OF RENAL FUNCTION... For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PENICILLIN G (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites About 16-30% of an intramuscular dose is metabolized to penicilloic acid, an inactive metabolite. Small amounts of 6-aminopenicillanic acid have been recovered in the urine of patients on penicillin G. A small percentage of the drug appears to be hydroxylated into one or more active metabolites, which are also excreted via urine. Approx 16-30% of an IM dose of penicillin G sodium is metabolized to penicilloic acid which is microbiologically inactive. Small amt of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) have also been found in the urine of patients receiving penicillin G. In addition, the drug appears to be hydroxylated to a small extent to one or more microbiologically active metabolites which are also excreted in urine. Biological Half-Life In adults with normal renal function is reportedly 0.4–0.9 hours ELIMINATION HALF-LIFE IS ABOUT 30 MIN IN NORMAL ADULTS. PENICILLIN HALF-LIFE IN HUMAN SERUM INCR FROM ABOUT 25 MIN IN YOUNG ADULTS TO 2 HR IN ELDERLY SUBJECTS & IS ALSO MARKEDLY INCR BY DRUGS WHICH ARE ACTIVELY SECRETED BY KIDNEY TUBULES. /PENICILLIN/ The serum half-life of penicillin G in adults with normal renal function is reportedly 0.4-0.9 hr. The serum half-life of penicillin G in neonates varies inversely with age and appears to be independent of birthweight. The serum half-life of the drug is reportedly 3.2-3.4 hr in neonates 6 days of age or younger, 1.2-2.2 hr in neonates 7-13 days of age, and 0.9-1.9 hr in neonates 14 days of age or older. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates that penicillin G produces low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with penicillins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Penicillin G is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A breastfed 1-month-old infant with congenital syphilis developed a Herxheimer reaction 6 hours after its mother received 2.4 million units of benzathine penicillin G intramuscularly. However, the baby had also received 10 units of penicillin G at about the same time as the mother's injection. The reaction was possibly caused by penicillin in breastmilk. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Bind to serum proteins (45-68%), mainly albumin. Interactions MARKED POTENTIATION OF HYPOPROTHROMBINEMIC EFFECT OF WARFARIN BY LARGE DOSES OF PARENTERAL PENICILLIN G DESCRIBED IN 49-YR-OLD MALE. PENICILLIN G CAUSED WARFARIN PROTEIN BINDING DISPLACEMENT INTERACTION. Penicillins are generally inactivated in the presence of heat, alkaline or acid pH, oxidizing agents, alcohols, glycols, and metal ions such as copper, mercury, or zinc. In currently available penicillins, cleavage at any point in the penicillin nucleus, including the beta-lactam ring, results in complete loss of antibacterial activity. The major cause of inactivation of penicillins is hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring. The course of hydrolysis and nature of the degradation products can vary and are generally influenced by pH. /Penicillins/ Penicillin G is potentially physically and/or chemically incompatible with some drugs, including aminoglycosides and tetracyclines, but the compatibility depends on several factors (eg, concn of the drugs, specific diluents used, resulting pH, temp). Penicillins are generally inactivated in the presence of heat, alkaline or acid pH, oxidizing agents, alcohols, glycols, and metal ions such as copper, mercury, or zinc. In currently available penicillins, cleavage at any point in the penicillin nucleus, including the beta-lactam ring, results in complete loss of antibacterial activity. The major cause of inactivation of penicillins is hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring. The course of hydrolysis and nature of the degradation products can vary and are generally influenced by pH. /Penicillins/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for PENICILLIN G (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Convulsants; GABA Modulators; Penicillins GINGIVOSTOMATITIS, PULMONARY INFECTIONS, & GENITAL DISEASE PRODUCED BY SYNERGISTIC ACTION OF FUSOBACTERIUM NUCLEATUM (FUSIFORM) & SPIROCHETES PRESENT IN RESPIRATORY TRACT ARE READILY TREATABLE WITH PENICILLIN. /PENICILLIN/ TWO MICROORGANISMS RESPONSIBLE FOR.../RAT-BITE FEVER/ ARE SENSITIVE TO PENICILLIN G. ...DRUG OF CHOICE IN MGMNT OF INFECTIONS DUE TO LIST MONOCYTOGENES... ONLY SPECIES OF PASTEURELLA HIGHLY SUSCEPTIBLE TO PENICILLIN IS PAST MULTOCIDA. ... CAUSATIVE AGENT OF /ERYSIPELOID/...IS SENSITIVE TO PENICILLIN. PENICILLIN G THERAPY OF SYPHILIS IS ALMOST IDEALLY SAFE, INEXPENSIVE, & HIGHLY EFFECTIVE. ...AGENT OF CHOICE FOR TREATMENT OF ALL CLINICAL FORMS OF ACTINOMYCOSIS...ANTHRAX...GAS GANGRENE... For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PENICILLIN G (35 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings WHEN MASSIVE DOSES OF PENICILLIN G SODIUM ARE USED, CONSIDERABLE SODIUM LOAD IS INTRODUCED, WHICH EXPANDS EXTRACELLULAR SPACE & MAY CAUSE EDEMA IN PT WITH HEART FAILURE. /PENICILLIN G SODIUM/ ALLERGIES CAN OCCUR TO PROCAINE COMPONENT, BUT OTHER TOXIC EFFECTS OF PROCAINE ARE VERY RARE. /PROCAINE/ ANURIA INCR HALF-LIFE OF PENICILLIN G FROM NORMAL VALUE OF 1/2 HR TO ABOUT 10 HR. ALTHOUGH PENICILLIN G PREPN FOR INHALATION THERAPY & FOR TOPICAL APPLICATION TO SKIN & MUCOUS MEMBRANES ARE STILL AVAIL, THEIR USE IS NOT RECOMMENDED BECAUSE PROOF THAT THEY ARE ADEQUATELY EFFECTIVE IS LACKING, & BECAUSE THEY PRODUCE HIGH INCIDENCE OF HYPERSENSITIZATION. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PENICILLIN G (23 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Penicillin G is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. The name "penicillin" can either refer to several variants of penicillin available, or to the group of antibiotics derived from the penicillins. Penicillin G has in vitro activity against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. The bactericidal activity of penicillin G results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis and is mediated through penicillin G binding to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs). Penicillin G is stable against hydrolysis by a variety of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases and extended spectrum beta-lactamases. |
| 分子式 |
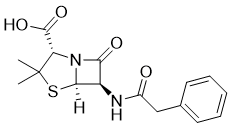
C16H18N2O4S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
334.4
|
| 精确质量 |
334.098
|
| CAS号 |
61-33-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Penicillin G potassium;113-98-4;Penicillin G sodium salt;69-57-8;Streptomycin;57-92-1;Penicillin G procaine hydrate;6130-64-9;Penicillin G benzathine;1538-09-6;Penicillin G benzathine tetrahydrate;41372-02-5;Penicillin G-d7 potassium;352323-25-2
|
| PubChem CID |
5904
|
| 外观&性状 |
AMORPHOUS WHITE POWDER
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
663.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
214-217 °C
214 - 217 °C |
| 闪点 |
355.0±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.655
|
| LogP |
1.67
|
| tPSA |
112.01
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
530
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
CC1([C@@H](N2C([C@@H](NC(CC3=CC=CC=C3)=O)[C@H]2S1)=O)C(O)=O)C
|
| InChi Key |
JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H18N2O4S/c1-16(2)12(15(21)22)18-13(20)11(14(18)23-16)17-10(19)8-9-6-4-3-5-7-9/h3-7,11-12,14H,8H2,1-2H3,(H,17,19)(H,21,22)/t11-,12+,14-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(2-phenylacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
Galofak CilopenBenzylpenicillin Pradupen
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9904 mL | 14.9522 mL | 29.9043 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5981 mL | 2.9904 mL | 5.9809 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2990 mL | 1.4952 mL | 2.9904 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。