| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
α1-adrenoceptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
特拉唑嗪不能区分在 COS 细胞中暂时表达的多种克隆 α1 肾上腺素能受体亚型 [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
对于输尿管结石的治疗,可以给予特拉唑嗪以促进结石转运。据观察,特拉唑嗪是一种安全有效的治疗远端输尿管结石的方法,尤其是那些直径超过 5 毫米的结石 [3]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
在当前的研究中,采用了各种鉴定技术来确定细胞毒性作用的作用方式。通过末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶脱氧尿苷三磷酸缺口末端标记,可以原位鉴定凋亡细胞。 PC-3细胞用100μM特拉唑嗪处理12小时后,结果显示阳性反应。
|
| 动物实验 |
Terazosin, a water-soluble alpha 1 antagonist that can be administered in high doses intraventricularly was used to study the relationship between brain alpha 1 adrenoceptor neurotransmission and behavioral activation in the mouse. The antagonist was found to produce a dose-dependent, complete inhibition of motor activity and catalepsy which were reversed preferentially by coinfusion of an alpha 1 agonist (phenylephrine) compared to a D1 (SKF38393) or a D2 agonist, (quinpirole). Blockade of central beta-1 (betaxolol), alpha-2 (RX821002) or beta-2 (ICI 118551) adrenoceptors had smaller or non-significant effects. Terazosin's selectivity for alpha 1 receptors versus dopaminergic receptors was verified under the present conditions by showing that the intraventricularly administered antagonist protected striatal and cerebral cortical alpha 1 receptors but not striatal or cortical D1 receptors from in vivo alkylation by N-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1, 2-dihydroxyquinoline. That its effect was due to blockade of brain rather than peripheral receptors was shown by the finding that intraperitoneal doses of terazosin three to 66 times greater than the maximal intraventricular dose produced less behavioral inhibition. Intraventricular terazosin also produced hypothermia and a reduced respiratory rate suggestive of a reduced sympathetic outflow. However, external heat did not affect the inactivity, and captopril, a hypotensive agent, did not mimic it. Terazosin did not impair performance on a horizontal wire test or the ability to make co-ordinated movements in a swim test suggesting that its activity-reducing effect was not due to sedation and may have a motivational or sensory gating component. It is concluded that central alpha 1-noradrenergic neurotransmission is required for behavioral activation to environmental change in the mouse and may operate on sensorimotor and motivational processes. Neuroscience. 1999;94(4):1245-52.
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Approximately 90%. Approximately 10% of the oral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine and approximately 20% is excreted in the feces. 40% of the total dose is eliminated in urine and 60% of the total dose is eliminated in the feces. 25L to 30L. Plasma clearance is 80mL/min and renal clearance is 10mL/min. Metabolism / Metabolites The majority of terazosin is hepatically metabolized. The metabolites recovered include 6-O-demethyl terazosin, 7-O-methyl terazosin, a piperozine derivative, and a diamine derivative. Hepatic. One of the four metabolites identified (piperazine derivative of terazosin) has antihypertensive activity. Route of Elimination: Approximately 10% of an orally administered dose is excreted as parent drug in the urine and approximately 20% is excreted in the feces. Half Life: 12 hours Biological Half-Life Terazosin has a mean half life 12 hours though this can be as high as 14 hours in patients over 70 years and as low as 11.4 hours in patients 20 to 39 years old. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Terazosin selectively and competitively inhibits vascular postsynaptic alpha(1)-adrenergic receptors, resulting in peripheral vasodilation and a reduction of vascular resistance and blood pressure. Unlike the nonselective alph-adrenergic blockers phenoxybenzamine and phentolamine, terazosin does not block presynaptic alpha(2)-receptors and, hence, does not cause reflex activation of norepinephrine release to produce reflex tachycardia. Hepatotoxicity Terazosin has been associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations that in controlled trials was no higher than with placebo therapy. These elevations were transient and did not require dose modification. Instances of serum enzyme elevations, but no instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury with jaundice due to terazosin, have been published. Furthermore, product labels do not include discussion of hepatic toxicity. Cholestatic hepatitis and jaundice have been reported with other alpha-adrenergic blockers. Thus, acute symptomatic liver injury due to terazosin must be exceedingly rare if it occurs at all. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because no information is available on the use of terazosin during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information in nursing mothers was not found as of the revision date. However, the pharmacologically similar drug prazosin does not affect serum prolactin concentration in patients with hypertension. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Protein Binding 90-94%. Toxicity Data LD50: 259.3mg/kg (parental-intravenous, Mouse) (A308) |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
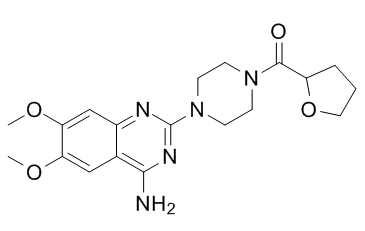
Terazosin is a member of quinazolines, a member of piperazines, a member of furans and a primary amino compound. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, an antihypertensive agent and an alpha-adrenergic antagonist.
Terazosin is a quinazoline derivative alpha-1-selective adrenergic blocking agent indicated for benign prostatic hyperplasia and hypertension. Terazosin blocks adrenaline's action on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, causing relaxation of smooth muscle in blood vessels and the prostate. Terazosin is an alpha-Adrenergic Blocker. The mechanism of action of terazosin is as an Adrenergic alpha-Antagonist. Terazosin is a nonselective alpha-1 adrenergic antagonist used in the therapy of hypertension and benign prostatic hypertrophy. Terazosin therapy is associated with a low rate of transient serum aminotransferase elevations and to rare instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Terazosin is a selective alpha 1 antagonist used for treatment of symptoms of prostate enlargement (BPH). It also acts to lower blood pressure, so it is a drug of choice for men with hypertension and prostate enlargement. It works by blocking the action of adrenaline on smooth muscle of the bladder and the blood vessel walls. See also: Terazosin Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Terazosin is indicated for use in treating symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia and hypertension. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Terazosin is selective for alpha-1-adrenoceptors but not their individual subtypes. Inhibition of these alpha-1-adrenoceptors results in relaxation of smooth muscle in blood vessels and the prostate, lowering blood pressure and improving urinary flow. Smooth muscle cells accounts for roughly 40% of the volume of the prostate and so their relaxation reduces pressure on the urethra. It has also been shown that catecholamines induce factors responsible for mitogenesis and alpha-1-adrenergic receptor blockers inhibit this effect. A final long term mechanism of terazosin and other alpha-1-adrenergic receptor blockers is the induction of apoptosis of prostate cells. Treatment with terazosin enhances the expression of transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-beta1), which upregulates p27kip1, and the caspase cascade. Pharmacodynamics Terazosin is a quinazoline derivative alpha-1-selective adrenergic blocker. |
| 分子式 |
C19H25N5O4ELEMENTALANALYSIS
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
387.43
|
| 精确质量 |
387.191
|
| CAS号 |
63590-64-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Terazosin hydrochloride dihydrate;70024-40-7;(R)-Terazosin;109351-34-0;(S)-Terazosin;109351-33-9;Terazosin hydrochloride;63074-08-8;Terazosin-d8;1006718-20-2
|
| PubChem CID |
5401
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.332 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
664.5ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
281-283°C
|
| 闪点 |
355.7ºC
|
| LogP |
1.64
|
| tPSA |
103.04
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
544
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
VCKUSRYTPJJLNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H25N5O4/c1-26-15-10-12-13(11-16(15)27-2)21-19(22-17(12)20)24-7-5-23(6-8-24)18(25)14-4-3-9-28-14/h10-11,14H,3-9H2,1-2H3,(H2,20,21,22)
|
| 化学名 |
[4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-(oxolan-2-yl)methanone
|
| 别名 |
Vasocard; terazosin; 63590-64-7; Terazosine; Fosfomic; Blavin; Flumarc; Vasomet; Terazosina; Hytrin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5811 mL | 12.9056 mL | 25.8111 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5162 mL | 2.5811 mL | 5.1622 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2581 mL | 1.2906 mL | 2.5811 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。